Printable Periodic Table Of Elements With Electron Configuration Pdf
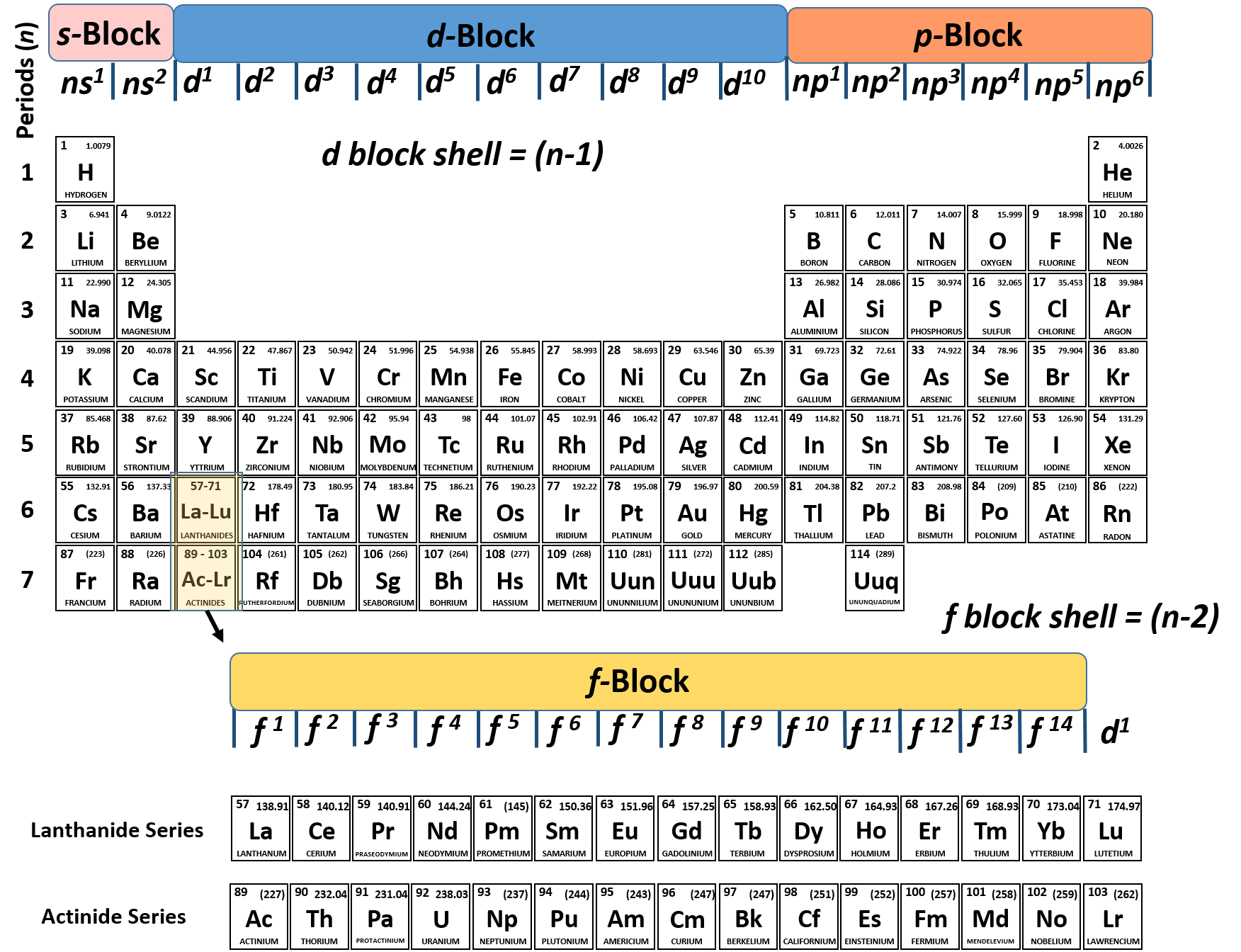
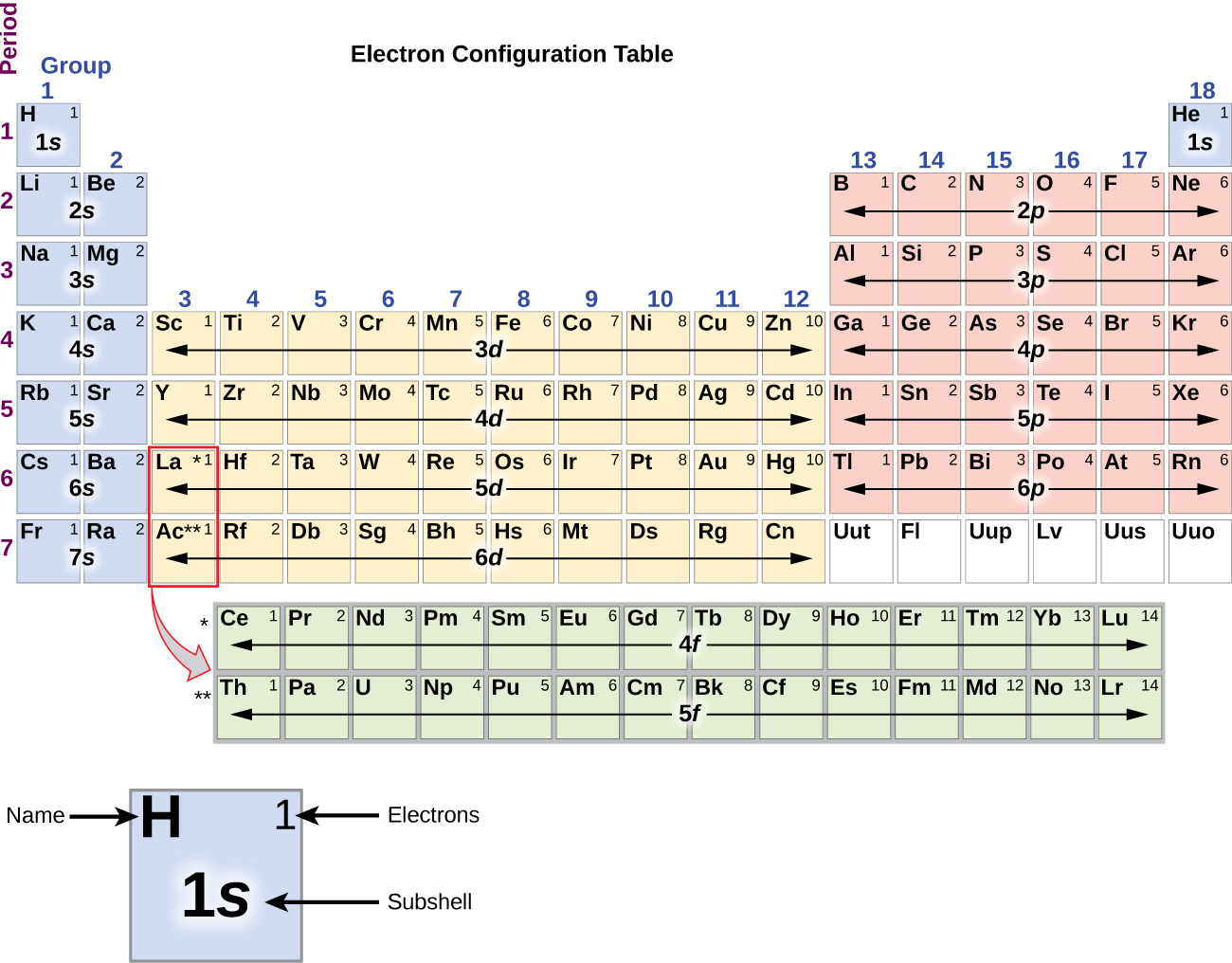
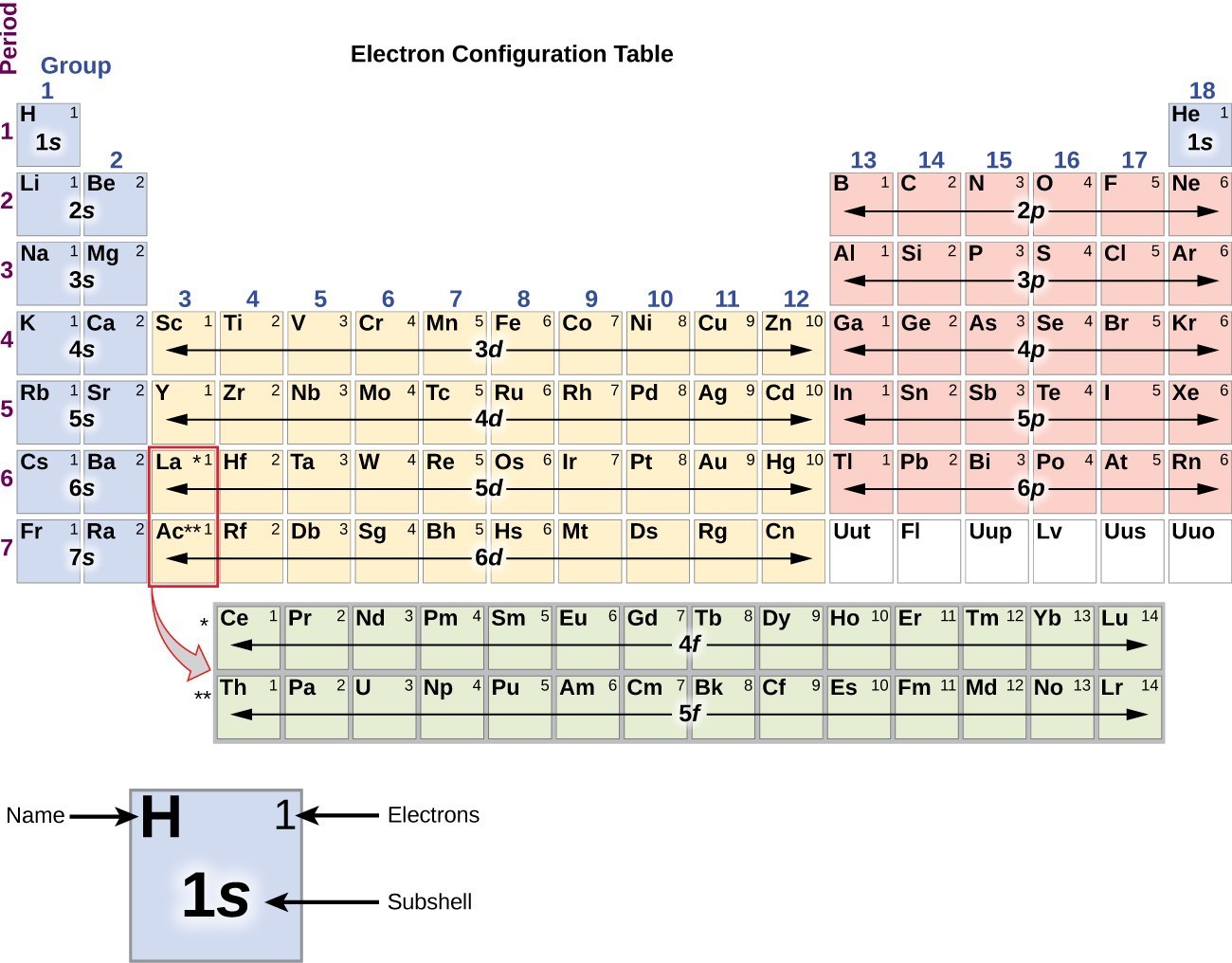
The arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom is called the electron configuration of the atom. We describe an electron configuration with a symbol that contains three pieces of information ( Figure 3.1.2 3.1. 2 ): The number of the principal quantum shell, n, The letter that designates the orbital type (the subshell, l ), and

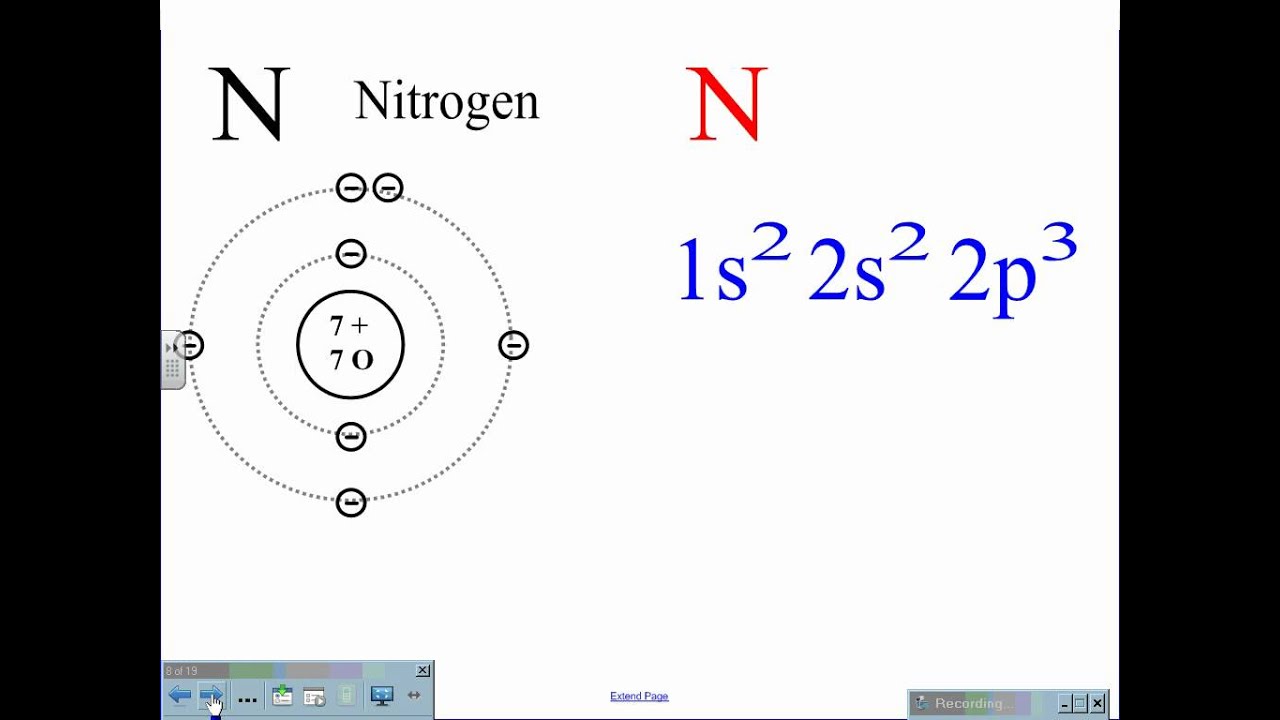
Nitrogen Electron Configuration YouTube
Electron configuration provides insight into the chemical behaviors of elements and is an important concept for students to master in introductory chemistry. To better strengthen undergraduate students' mastery of electron configurations of atoms and ions, we designed a novel, interactive chemistry game called ChemisTree that uses active-learning techniques (e.g., physically building.
Use The Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen To Write Quantum Numbers For The
Electron Configuration Notation: -shows the arrangment of electrons around the nucleus of an atom. - helps chemist understanding how elements form chemical bonds. - can be written using the period table or an electron configuration chart. How to Write the Electron Configuration for Nitrogen (N)
Sharing the Teachings Without Name and Number Urantia Book Urantia
The numbers of electrons that can occupy each shell and each subshell arise from the equations of quantum mechanics, [a] in particular the Pauli exclusion principle, which states that no two electrons in the same atom can have the same values of the four [2]
Valence Electrons & Electron Configurations YouTube
The arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom is called the electron configuration of the atom. We describe an electron configuration with a symbol that contains three pieces of information ( Figure 6.25 ): The number of the principal quantum shell, n,
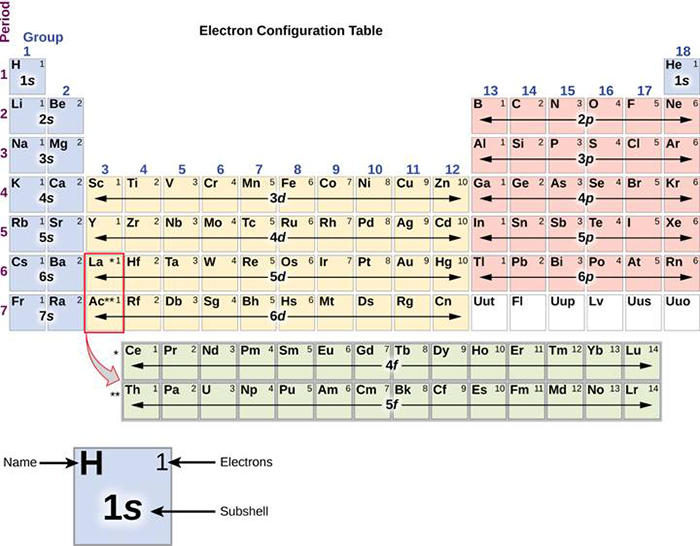
7.8B Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Chemistry LibreTexts
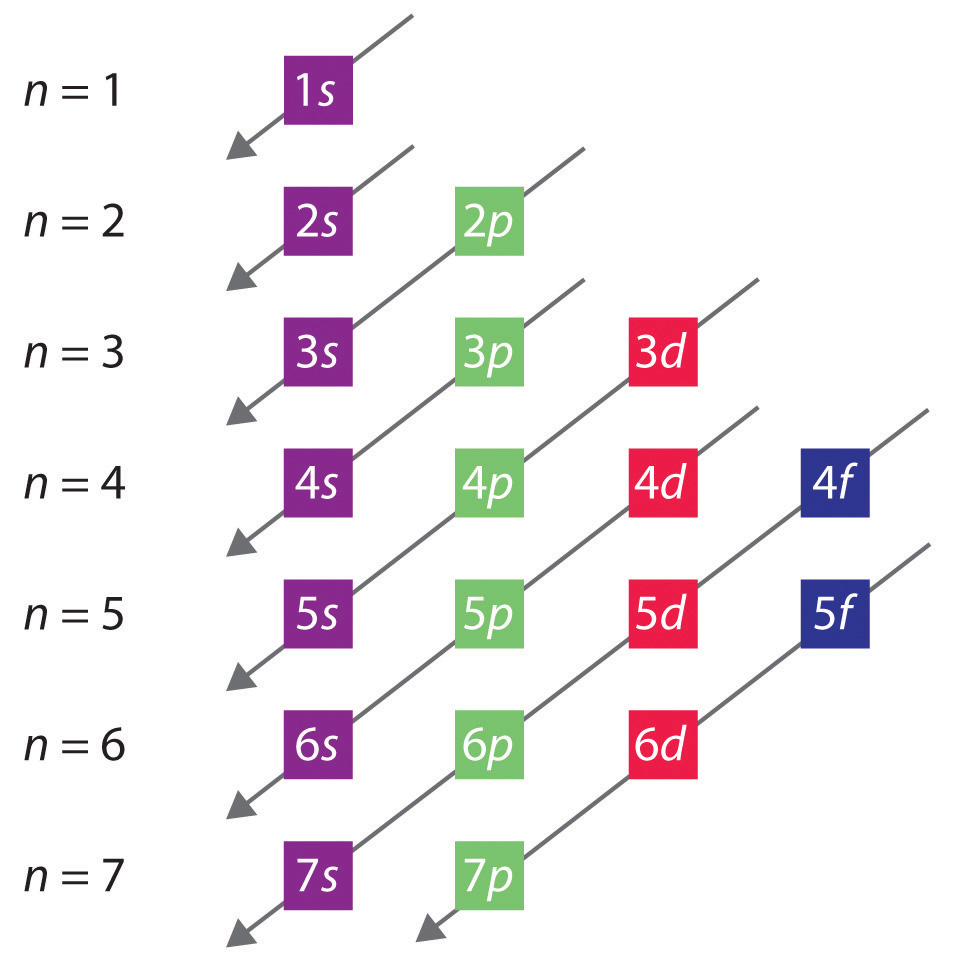
When writing the electron configuration for an atom, orbitals are filled in order of increasing atomic number. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. Example 3: 3 rd row elements. Following the pattern across a period from B (Z=5) to Ne (Z=10), the number of electrons increases and the subshells are filled.
6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations
This electron configuration calculator will instantly show you the distribution of electrons in the orbitals of any periodic element you choose. Typically, you need at least 8 steps to determine the electron configuration, starting with finding the atomic number by looking at the list of orbitals and understanding the notation.

Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen (N) Nitrogen Electron Configuration
1). You can effortlessly find every single detail about the elements from this single Interactive Periodic table. 2). You will get the detailed information about the periodic table which will convert a newbie into pro. 3). You will also get the HD images of the Periodic table (for FREE).
/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)
Electron Configuration Chart
Electron configurations are a simple way of writing down the locations of all of the electrons in an atom. As we know, the positively-charged protons in the nucleus of an atom tend to attract negatively-charged electrons.

Electron Configuration For Manganese Atomic Number 25 How Do You Draw
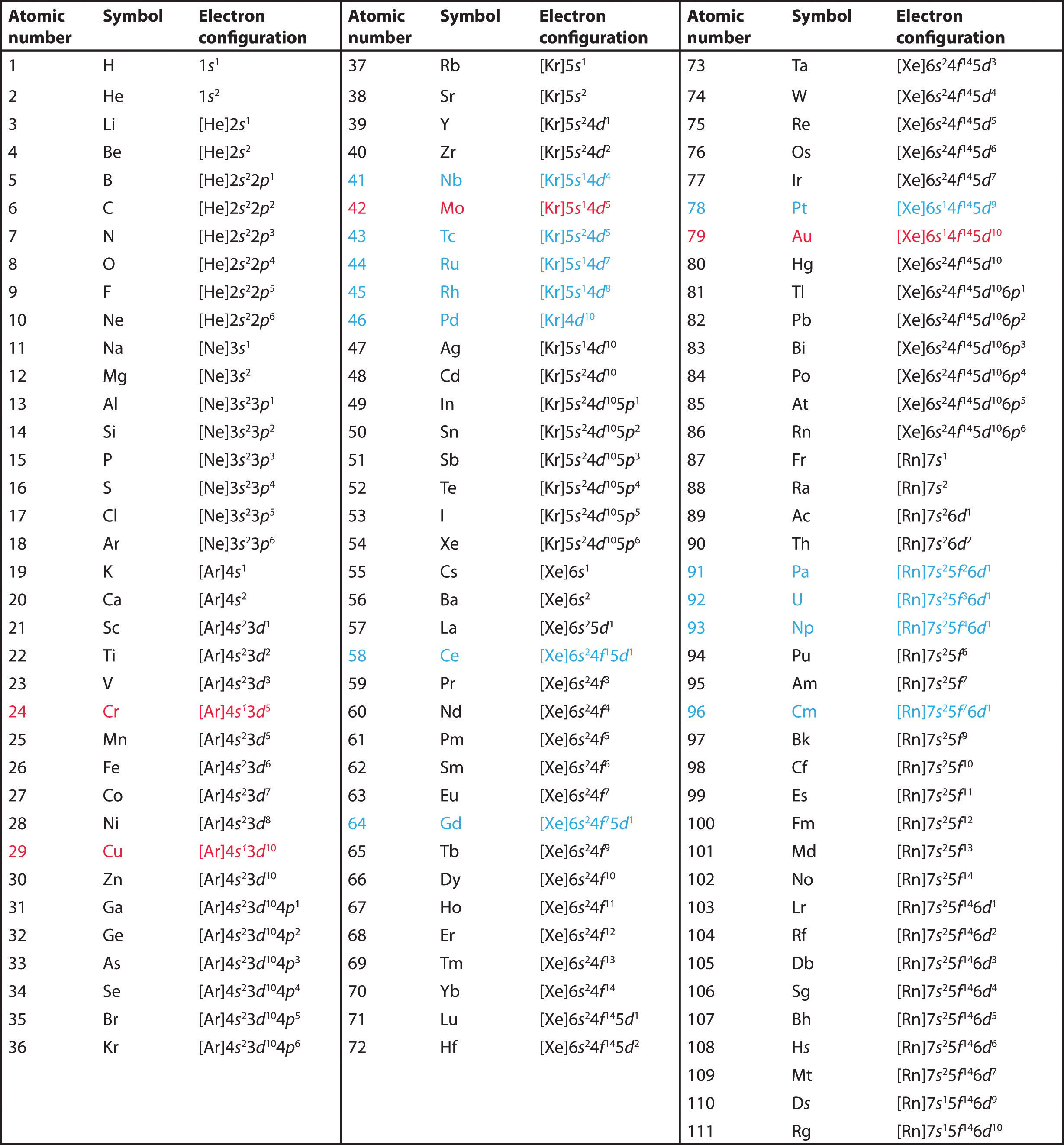
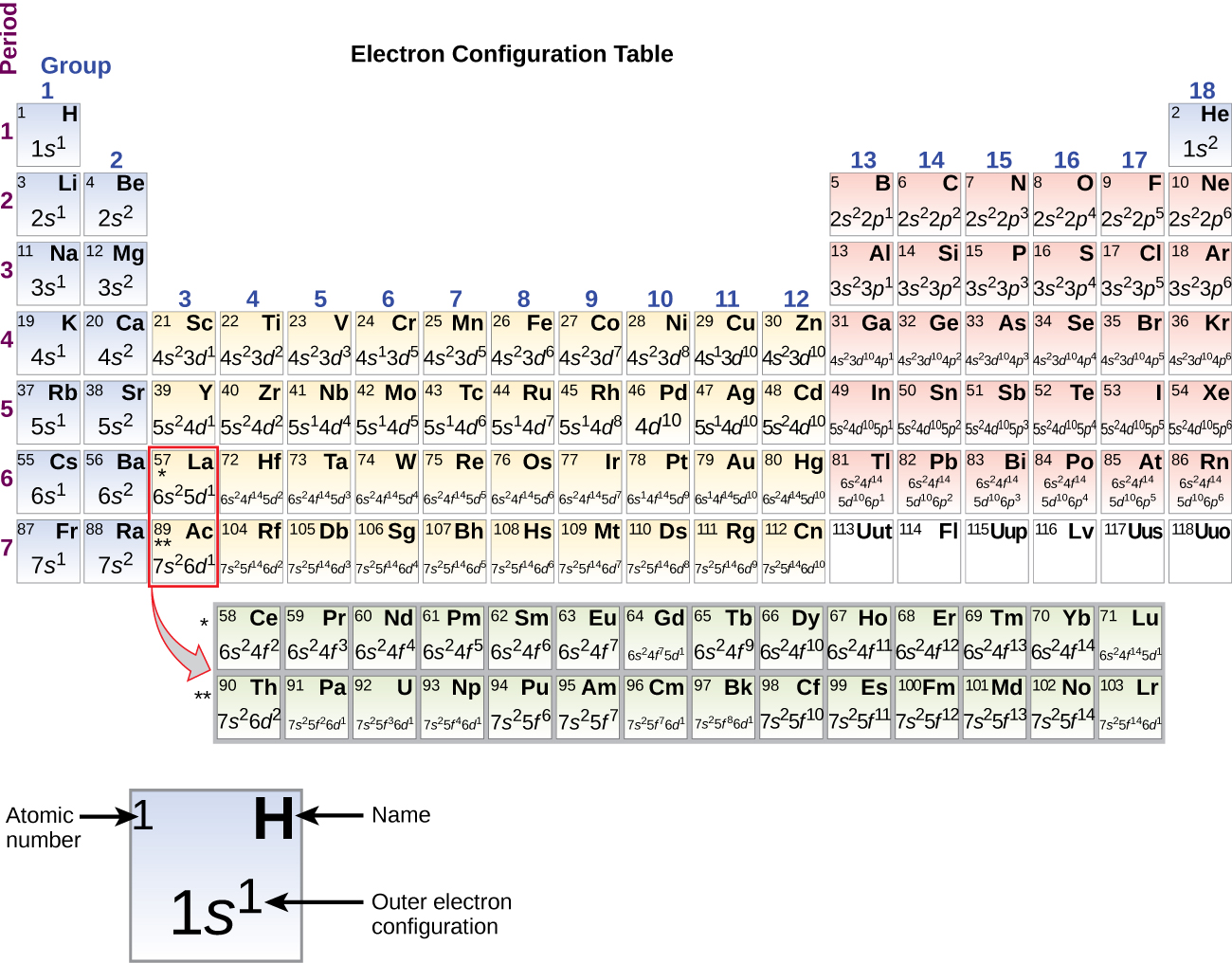
Answer: The electron configurations of the elements are presented in Figure 2.2.3, which lists the orbitals in the order in which they are filled. In several cases, the ground state electron configurations are different from those predicted by Figure 2.2.1. Some of these anomalies occur as the 3 d orbitals are filled.
Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations) Chemistry
The third major category of elements arises when the distinguishing electron occupies an f subshell. The first example occurs in the case of the lanthanoids (elements having atomic numbers between 57 and 71).The lanthanoids have the general electron configuration [Kr]4d 10 4f i 5s 2 5p 6 5d 0 or 1 6s 2. where i is a number between 0 and 14. Thus in the building-up process for the lanthanoids.
Question 9267e Socratic
In this case, 2+2+6+2+6+2+10+6+2+1= 39 and Z=39, so the answer is correct. A slightly more complicated example is the electron configuration of bismuth (symbolized Bi, with Z = 83). The periodic table gives the following electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p65s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p3.
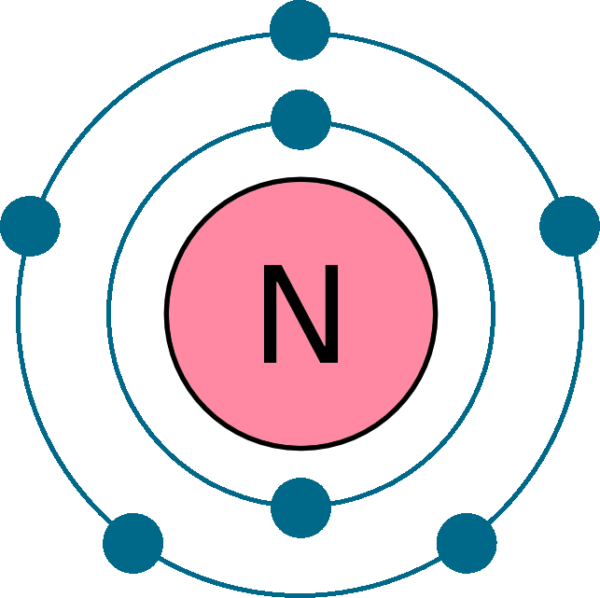
Nitrogen Element With Reaction, Properties, Uses, & Price Periodic Table
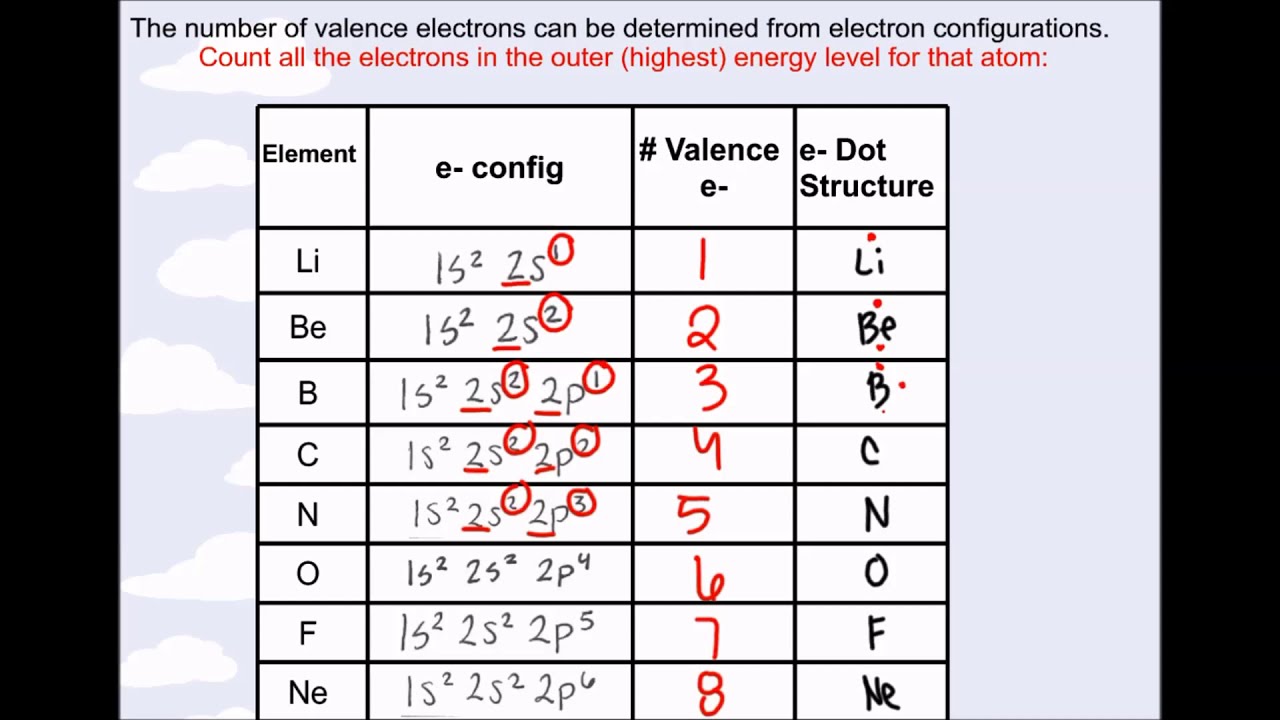
AboutTranscript. Electron configurations describe where electrons are located around the nucleus of an atom. For example, the electron configuration of lithium, 1s²2s¹, tells us that lithium has two electrons in the 1s subshell and one electron in the 2s subshell. Created by Sal Khan.
Electron Configurations YouTube
The same rule will apply to transition metals when forming ions. You should note that the ns electrons are always lost before the (n-1)d when forming cations for transition metals.For example, the electron configuration for Zn: [Ar]4s 2 3d 10 . the electron configuration for Zn +2: [Ar]3d 10 . The transition metals still do not end up being isoelectronic with a noble gas, but the loss of two.
Electron Configurations, Orbital Box Notation (M7Q7) UWMadison
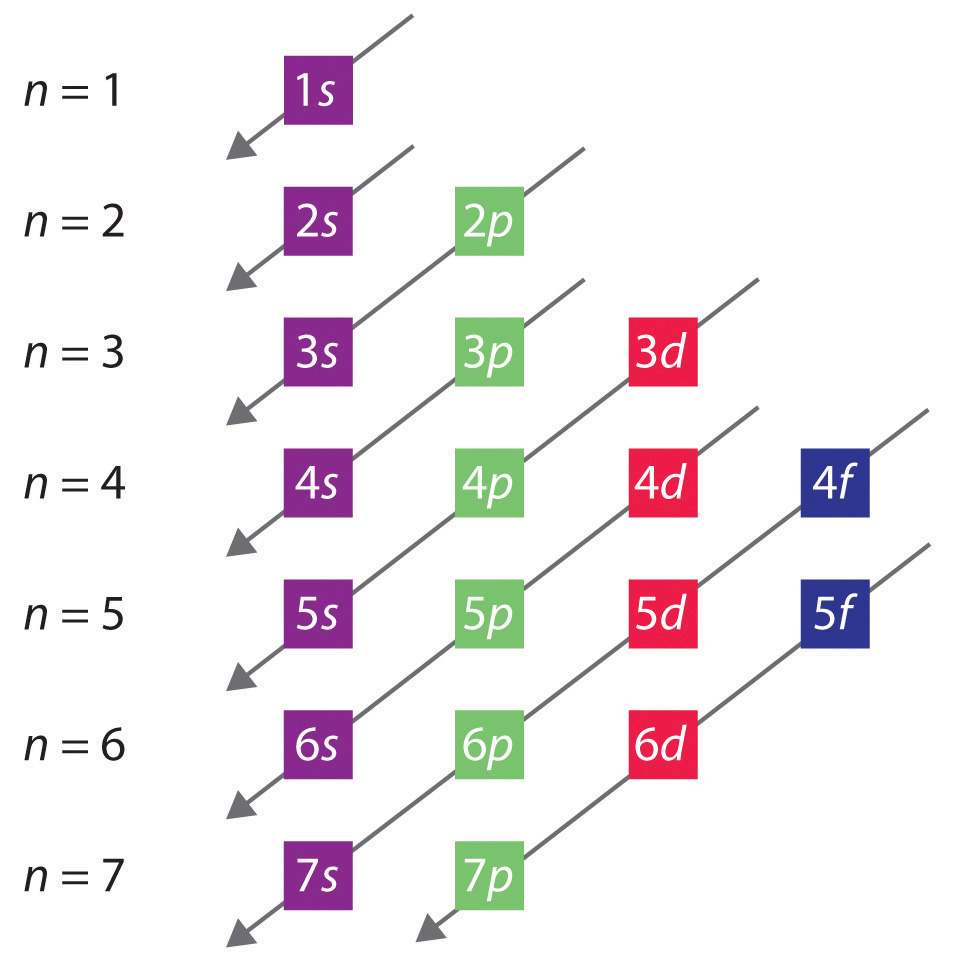
Principal Quantum Number (n) The principal quantum number n indicates the shell or energy level in which the electron is found. The value of n can be set between 1 to n, where n is the value of the outermost shell containing an electron. This quantum number can only be positive, non-zero, and integer values. That is, n=1,2,3,4,.. For example, an Iodine atom has its outmost electrons in the 5p.

Electronic Configurations Intro Chemistry LibreTexts
Electron Configurations are an organized means of documenting the placement of electrons based upon the energy levels and orbitals groupings of the periodic table.. The electron configuration for the first 10 elements. H #1s^1# He #1s^2# Li #1s^2 2s^1# Be #1s^2 2s^2# B #1s^2 2s^2 2p^1# C #1s^2 2s^2 2p^2# N #1s^2 2s^2 2p^3# O #1s^2 2s^2 2p^4# F #1s^2 2s^2 2p^5#