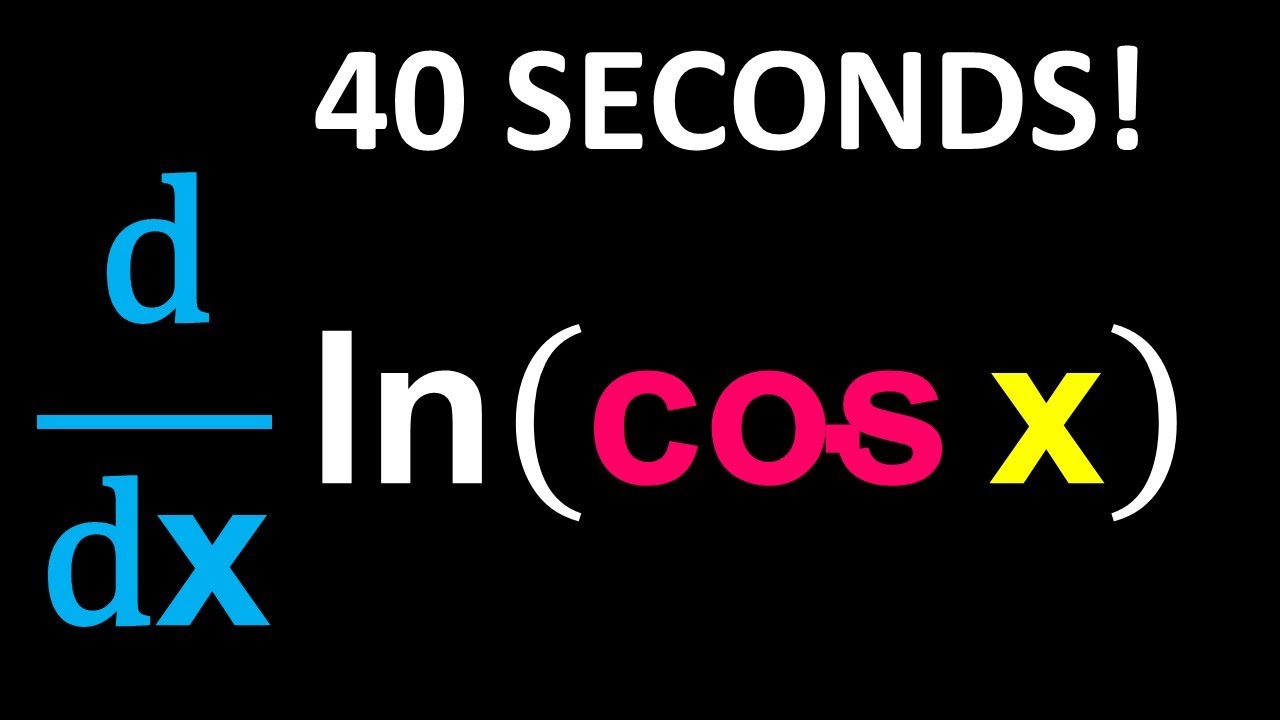
Derivative of ln(cos(x)) done in 40 seconds! YouTube
Integration by Parts: Integral of cos(ln x) dx#calculus #integral #integrals #integration #integrationbyparts

Integration by Parts Integral of cos(ln x) dx YouTube
integral of cos (ln (x)) with u sub: @0:00 integral of cos (ln (x)) without u sub, @8:20subscribe to @bprpcalculus for more calculus tutorialsCheck out my 100 in.

Indefinite integeral of (cos(Lnx)) / x YouTube
so basically the derivative of a function has the same domain as the function itself. Therefore the derivative of the function f (x)= ln (x), which is defined only of x > 0, is also defined only for x > 0 (f' (x) = 1/x where x > 0). i hope this makes sense. ( 2 votes)
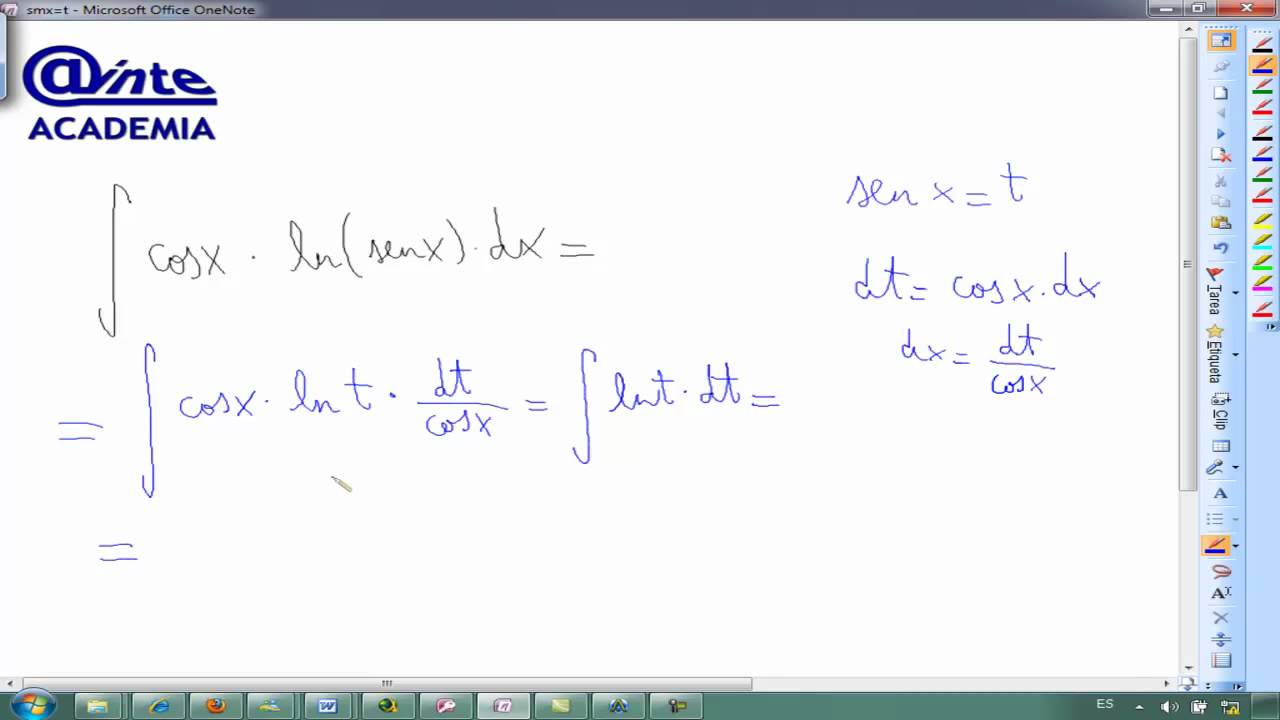
Integral cosx ln cos x Matematicas 2º Bachillerato AINTE YouTube
Trigonometry Free math problem solver answers your trigonometry homework questions with step-by-step explanations.
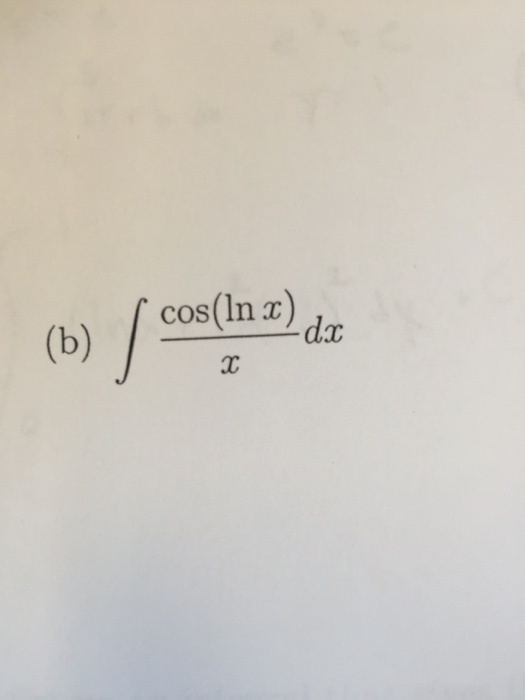
Solved integral cos(ln x)/x dx
The integral of cos (lnx) is an antiderivative of cos (ln x) function which is equal to ½ [xsin (ln x) + xcos (ln x)]. It is also known as the reverse derivative of sine function which is a trigonometric identity. The sine function is the ratio of adjacent side to the hypotenuse of a triangle which is written as: cos = adjacent side / hypotenuse
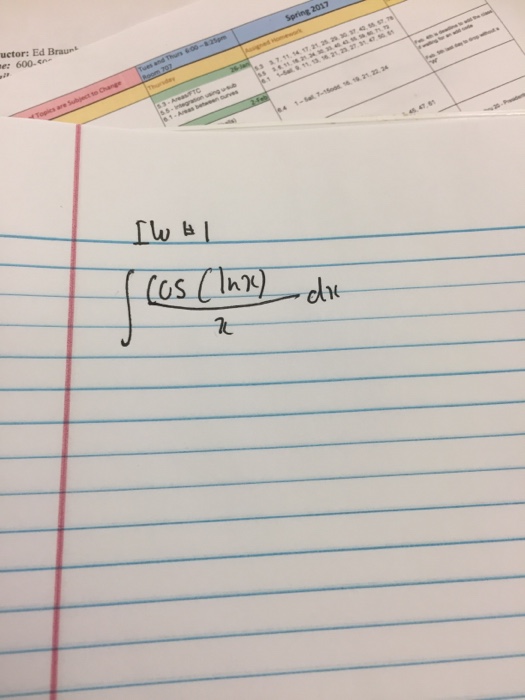
Solved integral cos (ln x)/x dx
WolframAlpha Online Integral Calculator Solve integrals with Wolfram|Alpha x sin x2 d x Natural Language Math Input More than just an online integral solver Wolfram|Alpha is a great tool for calculating antiderivatives and definite integrals, double and triple integrals, and improper integrals.

IMPORTANT Substitution and Integration and Parts to find Integral cos
.more 🏼 https://integralsforyou.com - Integral of cos (ln (x)) - How to integrate it step by step using integration by parts!🔍 𝐀𝐫𝐞 𝐲𝐨𝐮 𝐥𝐨𝐨𝐤𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐟𝐨𝐫.

Integration by Parts the Integral of cos(ln(x)) YouTube
1 Answer Jim H Aug 30, 2015 Integrate by parts (twice). Explanation: Looking at ∫cos(lnx)dx, we realize that if can't integrate straight away. Next thought is, perhaps we could use substitution. We would need cos(lnx) 1 x to integrate by substitution.

Pin on Integration Videos
Free Pre-Algebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators step-by-step
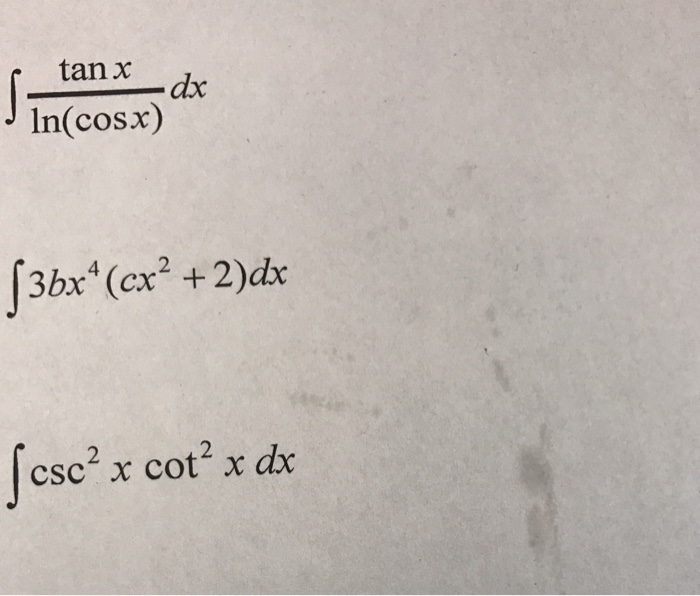
Solved integral tan x/ln(cos x) dx integral 3 bx^4 (cx^2 +
Please Subscribe here, thank you!!! https://goo.gl/JQ8NysIntegration by Parts the Integral of cos(ln(x))

Integral of cos(ln(x)) (by parts) YouTube
Integral of cos(ln(x))/x - How to integrate it step by step using the substitution method! Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/integralsforyou?sub_confirmation.
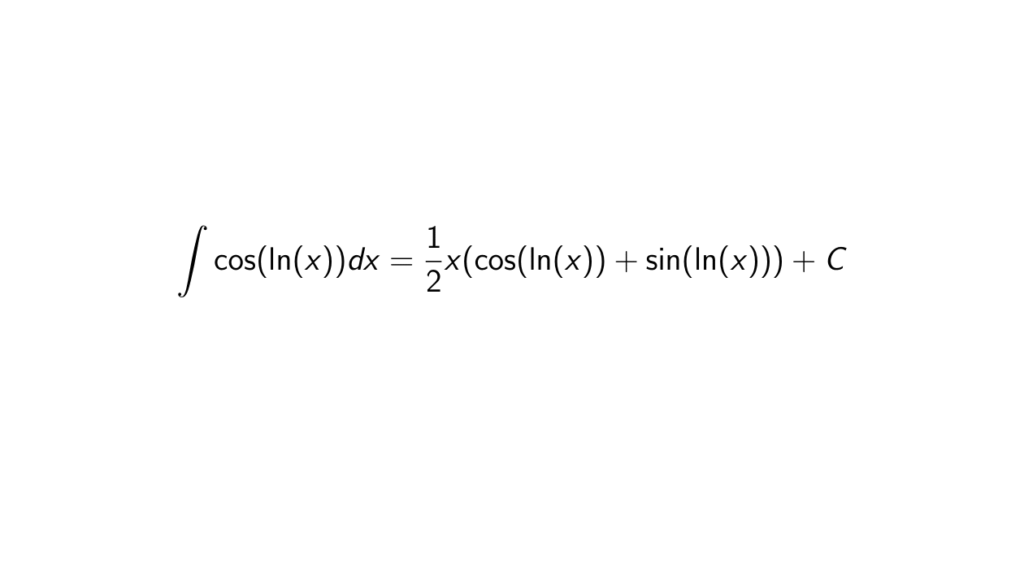
What is the integral of cos(ln(x))? Epsilonify
Free derivative calculator - differentiate functions with all the steps. Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph
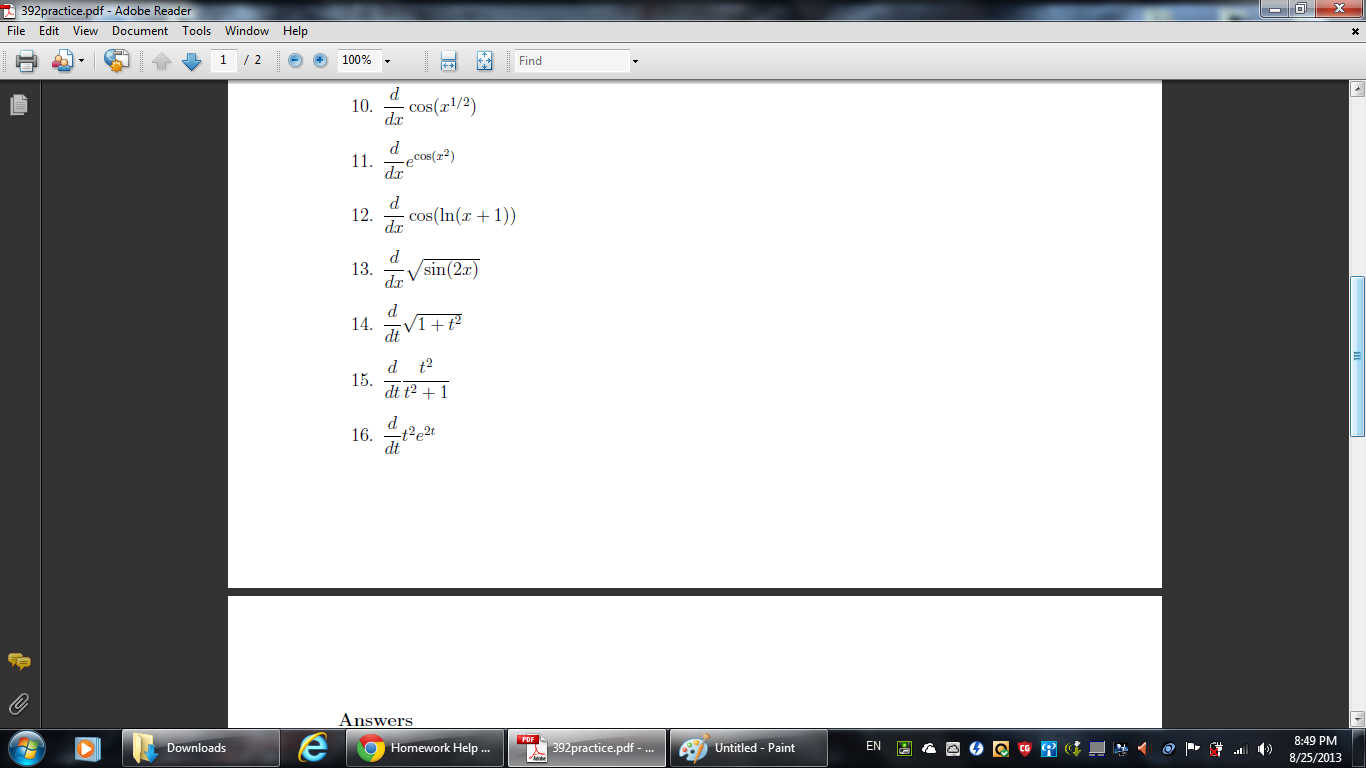
Solved d/dx cos(x1/2) d/dxecos(x2) d/dx cos(ln(x + 1))
Example 3.5.2: Finding the Derivative of a Function Containing cos x. Find the derivative of g(x) = cosx 4x2. Solution. By applying the quotient rule, we have. g′ (x) = ( − sinx)4x2 − 8x(cosx) (4x2)2. Simplifying, we obtain. g′ (x) = − 4x2sinx − 8xcosx 16x4 = − xsinx − 2cosx 4x3.
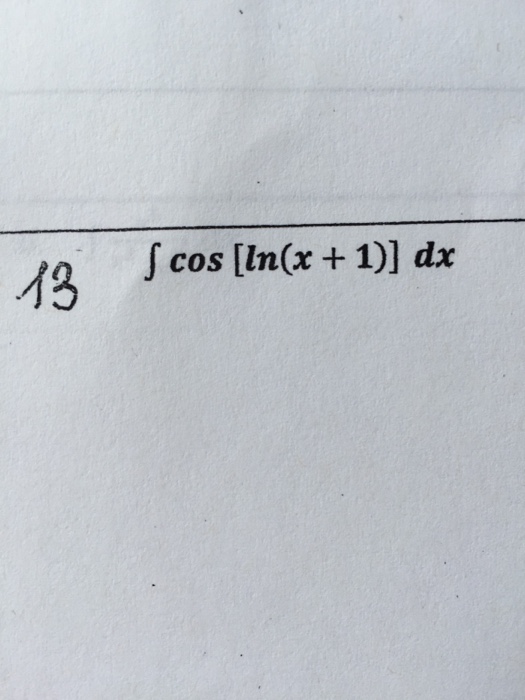
Solved Integral cos [ln(x + 1)dx
Arithmetic Matrix Simultaneous equation Differentiation Integration Limits Solve your math problems using our free math solver with step-by-step solutions. Our math solver supports basic math, pre-algebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.
Cos(ln x) dx = 11_(a) sin (In x) + c(b) COS (In x) + … SolvedLib
Figure 7.1.1: To find the area of the shaded region, we have to use integration by parts. For this integral, let's choose u = tan − 1x and dv = dx, thereby making du = 1 x2 + 1 dx and v = x. After applying the integration-by-parts formula (Equation 7.1.2) we obtain. Area = xtan − 1x|1 0 − ∫1 0 x x2 + 1 dx.

d/dx x*cos(ln(x)) by product and chain rule derivatives x*cos(ln(x
Figure 6.2.7: Setting up Integration by Parts. Putting this all together in the Integration by Parts formula, things work out very nicely: $$\int \ln x\,dx = x\ln x - \int x\,\frac1x\,dx.\] The new integral simplifies to ∫ 1dx, which is about as simple as things get. Its integral is x + C and our answer is.