
Question Video Calculating the de Broglie Wavelength of a Particle Nagwa
De Broglie Wavelength Formula is a formula that defines the nature of a wave to that of a particle. Many experiments show that light can behave both as a wave and as a particle. The particles of light are known as photons.
PPT Chapter 5 PowerPoint Presentation ID6630200
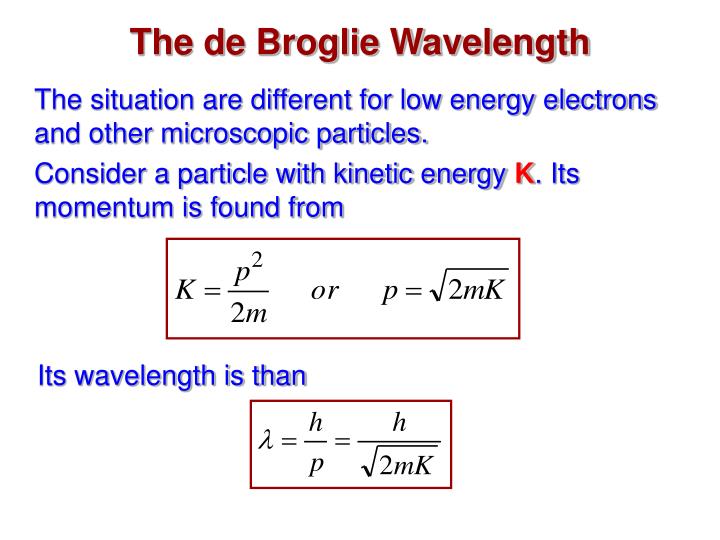
Solution: Reasoning: The de Broglie wavelength of an object is defined as λ = h/p. Details of the calculation: λ = h/p, E = p 2 / (2m), p = √ (2mE), λ = h/√ (2mE). The energy of the electron is 25000 eV * 1.6*10 -19 J/eV = 4*10 -15 J. λ = (6.626*10 -34 Js)/√ (2*9.1*10 -31 kg*4*10 -15 J) = 7.8*10 -12 m.

PPT Chapter 5 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3201239
Compton's formula established that an electromagnetic wave can behave like a particle of light when interacting with matter. In 1924, Louis de Broglie proposed a new speculative hypothesis that electrons and other particles of matter can behave like waves. Today, this idea is known as de Broglie's hypothesis of matter waves.In 1926, De Broglie's hypothesis, together with Bohr's early.

Question Video Relating Momentum to the de Broglie Wavelength Nagwa
De Broglie hypothesis Propagation of de Broglie waves in one dimension - real part of the complex amplitude is blue, imaginary part is green. The probability (shown as the color opacity) of finding the particle at a given point x is spread out like a waveform; there is no definite position of the particle.
de Broglie equation Science, quantum theory ShowMe
To determine the de Broglie wavelength of a particle given its mass and velocity, you need to: Multiply the velocity by mass. Their product is the particle's momentum. Divide Planck's constant by the momentum found in Step 1. The result you've got is exactly the de Broglie wavelength of your particle. Congrats!

De Broglie's Formula YouTube
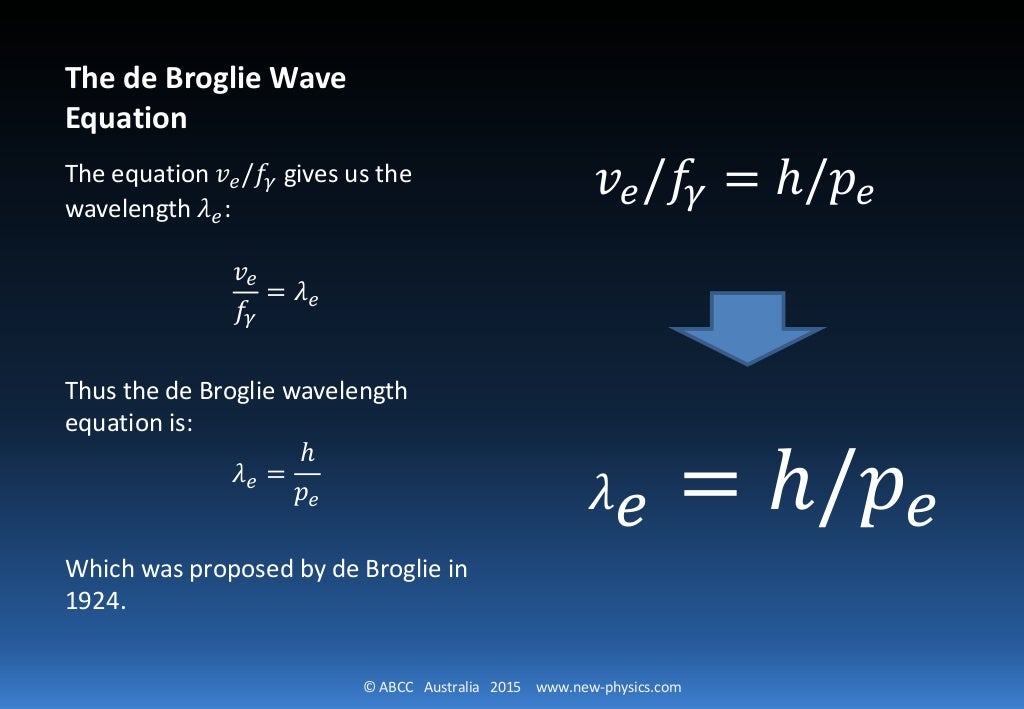
Through the equation λ λ, de Broglie substituted v/λ v / λ for ν ν and arrived at the final expression that relates wavelength and particle with speed. mv2 = hv λ (5) (5) m v 2 = h v λ. Hence. λ = hv mv2 = h mv (6) (6) λ = h v m v 2 = h m v. A majority of Wave-Particle Duality problems are simple plug and chug via Equation 6 6 with.

de Broglie Equation — Overview & Calculations Expii
This chemistry video tutorial explains how to calculate the de broglie wavelength of large objects and small particles such as electrons. It contains plenty.

The De Broglie Wavelength Equation YouTube
De Broglie Wavelength Matter waves are the central part of the theory of quantum mechanics. All matter can exhibit wave-like behaviour. The concept that matter behaves like a wave this concept was proposed by a French physicist named Louis de Broglie in the year 1924. It is also known as the de Broglie hypothesis.
What is the significance of de Broglie's equation? Quora
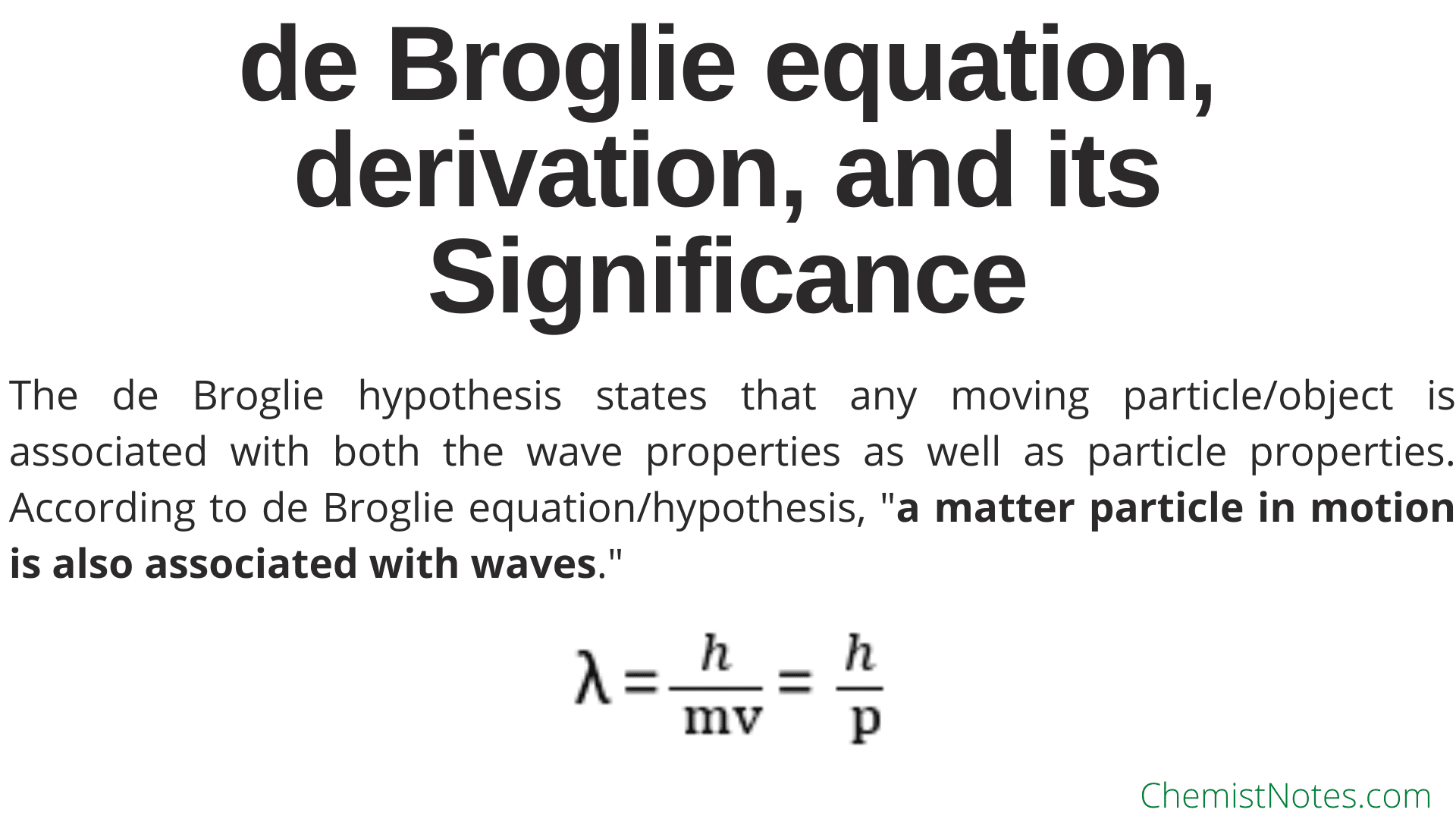
The de Broglie equation is an equation used to describe the wave properties of matter, specifically, the wave nature of the electron : λ = h/mv, where λ is wavelength, h is Planck's constant, m is the mass of a particle, moving at a velocity v. de Broglie suggested that particles can exhibit properties of waves.

De Broglie Wavelength Formula Equation, Concept, Solved Examples
Now comes the second equation. It is one of two related equations called the de Broglie equations. You can read more about de Broglie's work here. He received the 1929 Nobel Prize in Physics for this work. (I will discuss the second de Broglie equation below the following example problems.) Equation Number Two: λ = h/p

Question Video Identifying the de Broglie Relationship Nagwa
Is it a particle or a wave? This is the question that physicists of the 1920s were asking about light. In 1924, Louis de Broglie took this question to another level as he explored how electrons - which are matter, and were thought to be simply particles - can behave like waves. Questions Tips & Thanks Sort by: Top Voted Patrick 7 years ago

Question Video Calculating the de Broglie Wavelength of an Electron
In 1924, French scientist Louis de Broglie derived an equation, known as the De Broglie Wavelength Formula, that described the wave nature of any particle. Thus, establishing the wave-particle duality for the matter. Microscopic particle-like electrons also proved to possess this dual nature property.
PM [D02] de Broglie deriving the Equation
The de Broglie equation is one of the equations that is commonly used to define the wave properties of matter. It basically describes the wave nature of the electron. Electromagnetic radiation exhibits the dual nature of a particle (having a momentum) and wave (expressed in frequency and wavelength).
De Broglie wave equation Derivation by SK
De Broglie Wavelength Formula is used to calculate the wavelength and momentum in any given problems based on this concept. Solved Examples Question 1: Find the wavelength of an electron moving with a speed of ms-1. Solution: Given: Velocity of the electron, v =2 ×106 ms-1 Mass of electron, m =9.1 ×10-31 Kg

PPT Chapter 27 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2929126
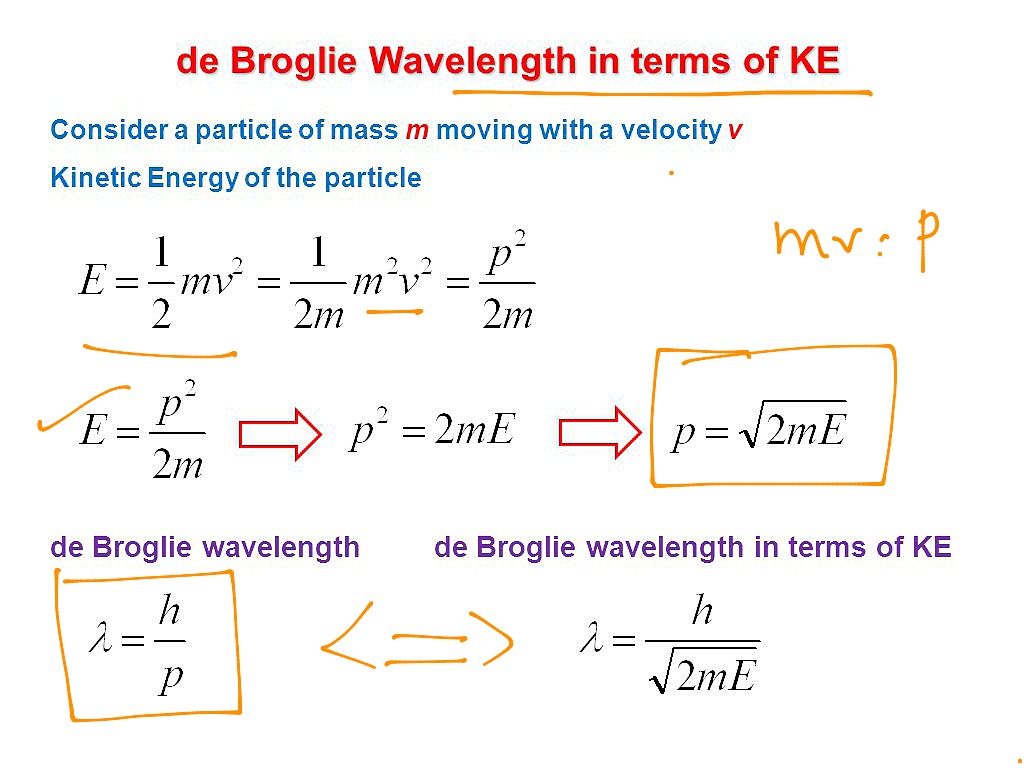
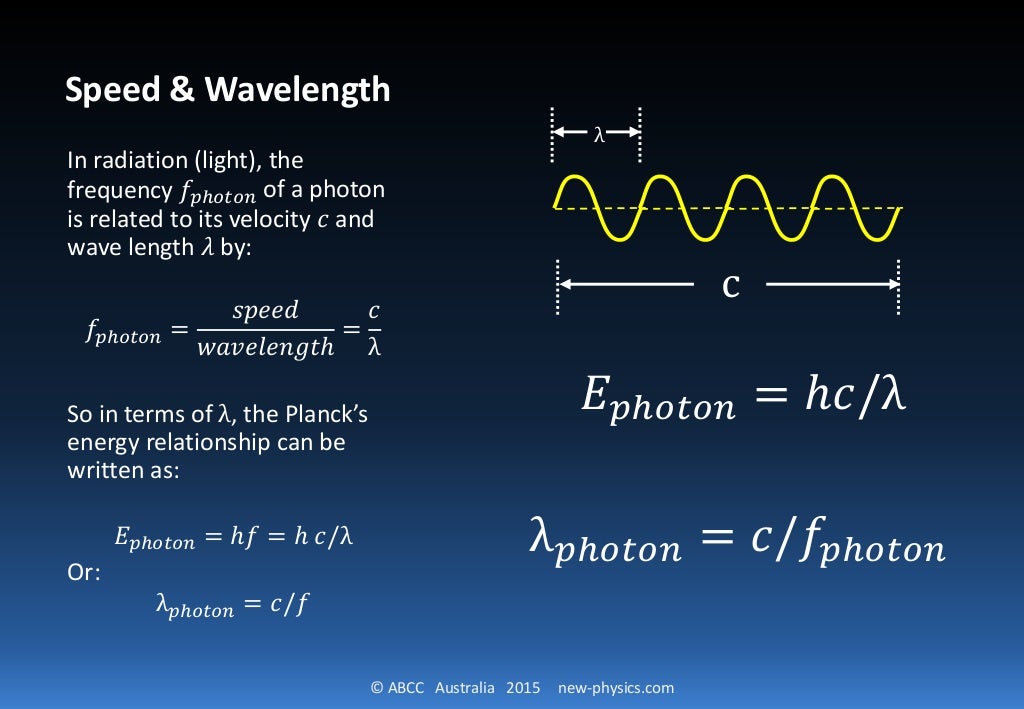
Derivation de Broglie derived the above relationship as follows: 1) E = hν for a photon and λν = c for an electromagnetic wave. 2) E = mc 2, means λ = h/mc, which is equivalent to λ = h/p. Note: m is the relativistic mass and not the rest mass since the rest mass of a photon is zero.
de Broglie equation, derivation, and its Significance Chemistry Notes
De Broglie was able to mathematically determine what the wavelength of an electron should be by connecting Albert Einstein's mass-energy equivalency equation (E = mc 2) with Planck's equation (E = hf), the wave speed equation (v = λf ) and momentum in a series of substitutions.