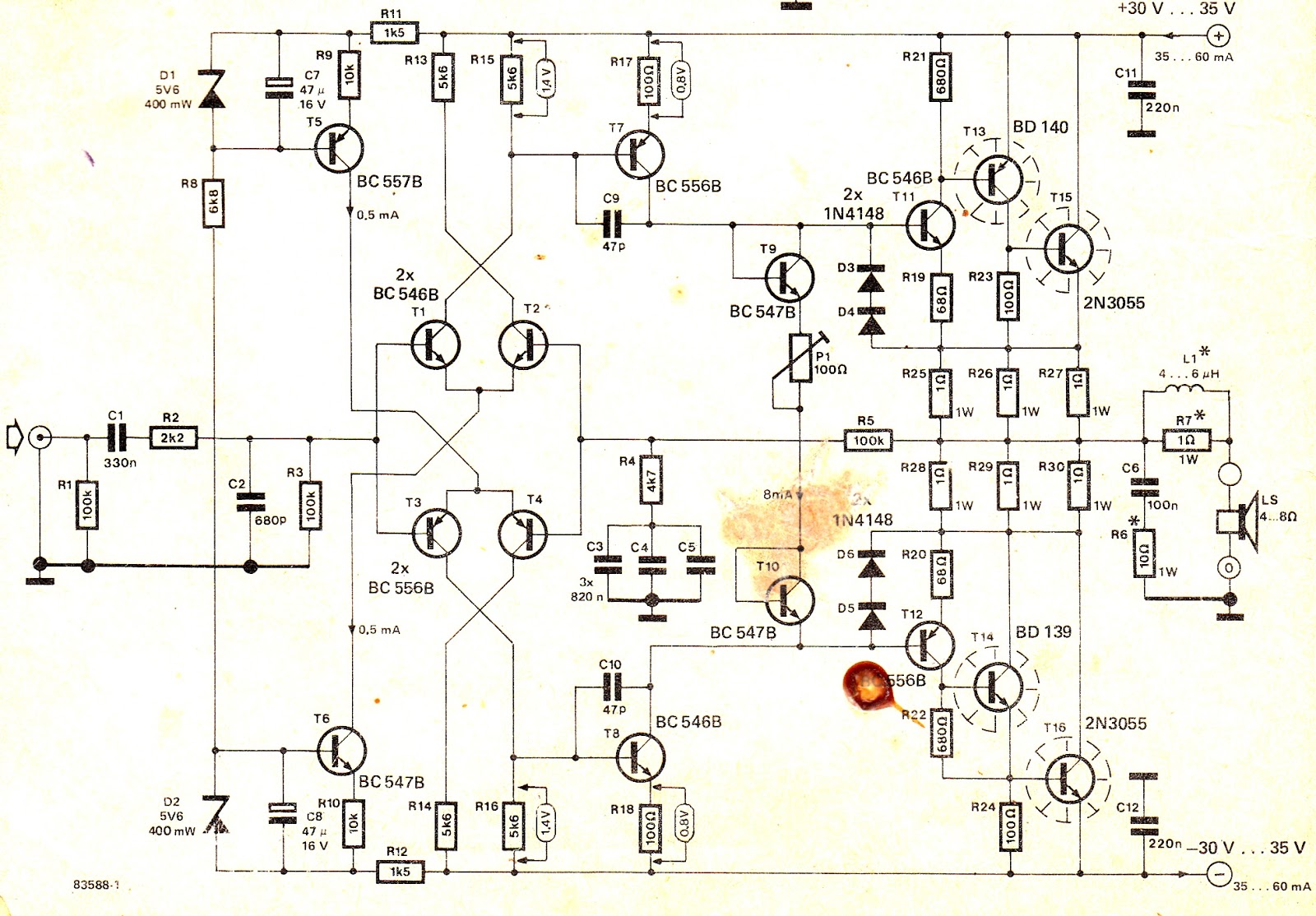
How to Make a HiFi 100 Watt Amplifier Circuit Using 2N3055 Transistors
Transistor as an Amplifier - Circuit Diagram, and Its Working A transistor is a three terminal semiconductor device, and the terminals are E (Emitter), B (Base) & C (Collector). The transistor can work in three different regions like active region, cutoff region & saturation region.
Darlington Transistor Amplifier Circuit Diagram IOT Wiring Diagram
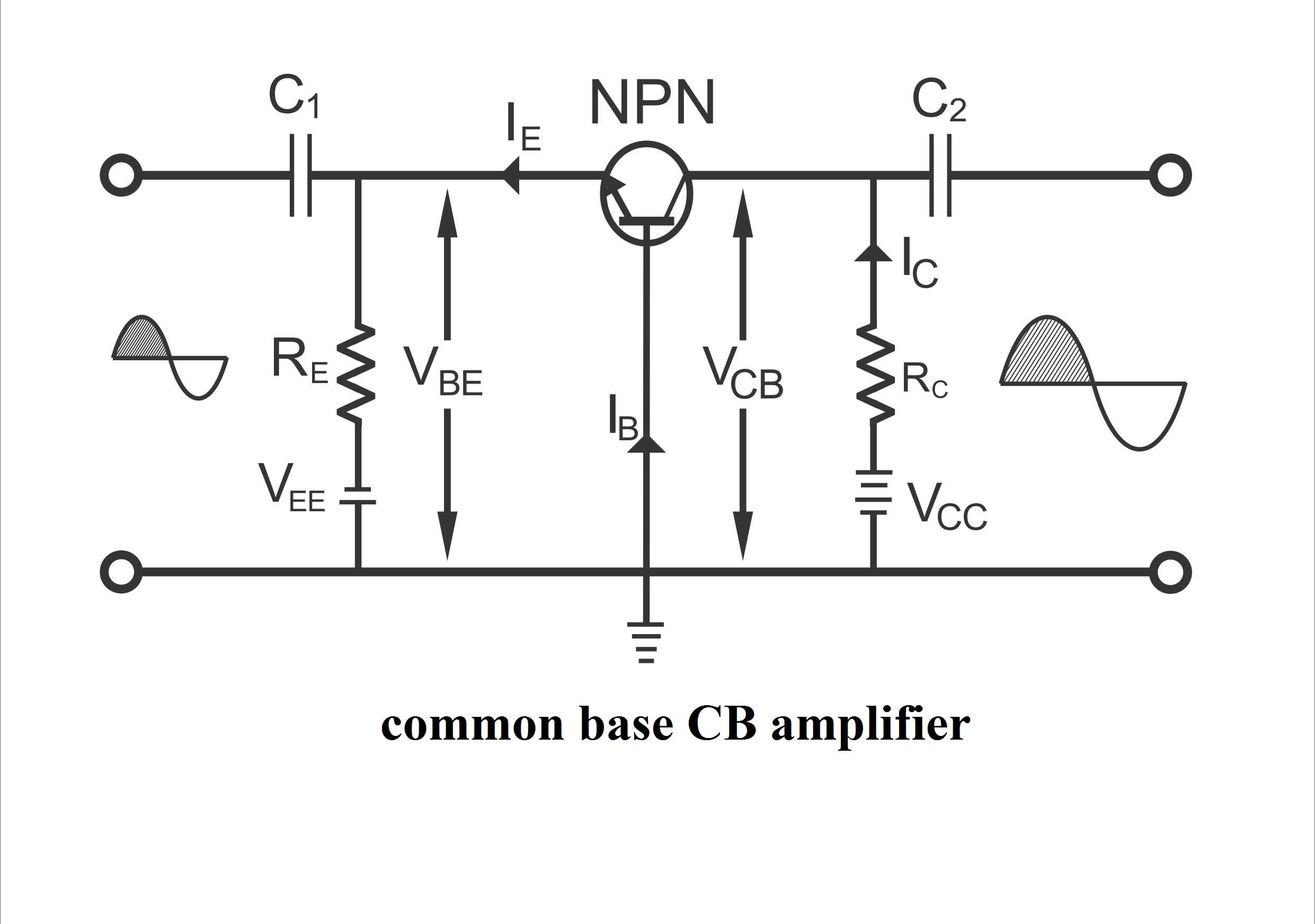
Basic Electronics Transistor as an Amplifier Working and Circuit Diagrams Engr Fahad April 26, 2022 2,619 Table of Contents BJT APPLICATIONS BJT Appliances Common Base (CB) Amplifier Circuit Operation of CB Amplifier Characteristics of a CB Amplifier Uses Common Emitter (CE) Amplifier Circuit Operation of CE Amplifier Current Gain Voltage Gain
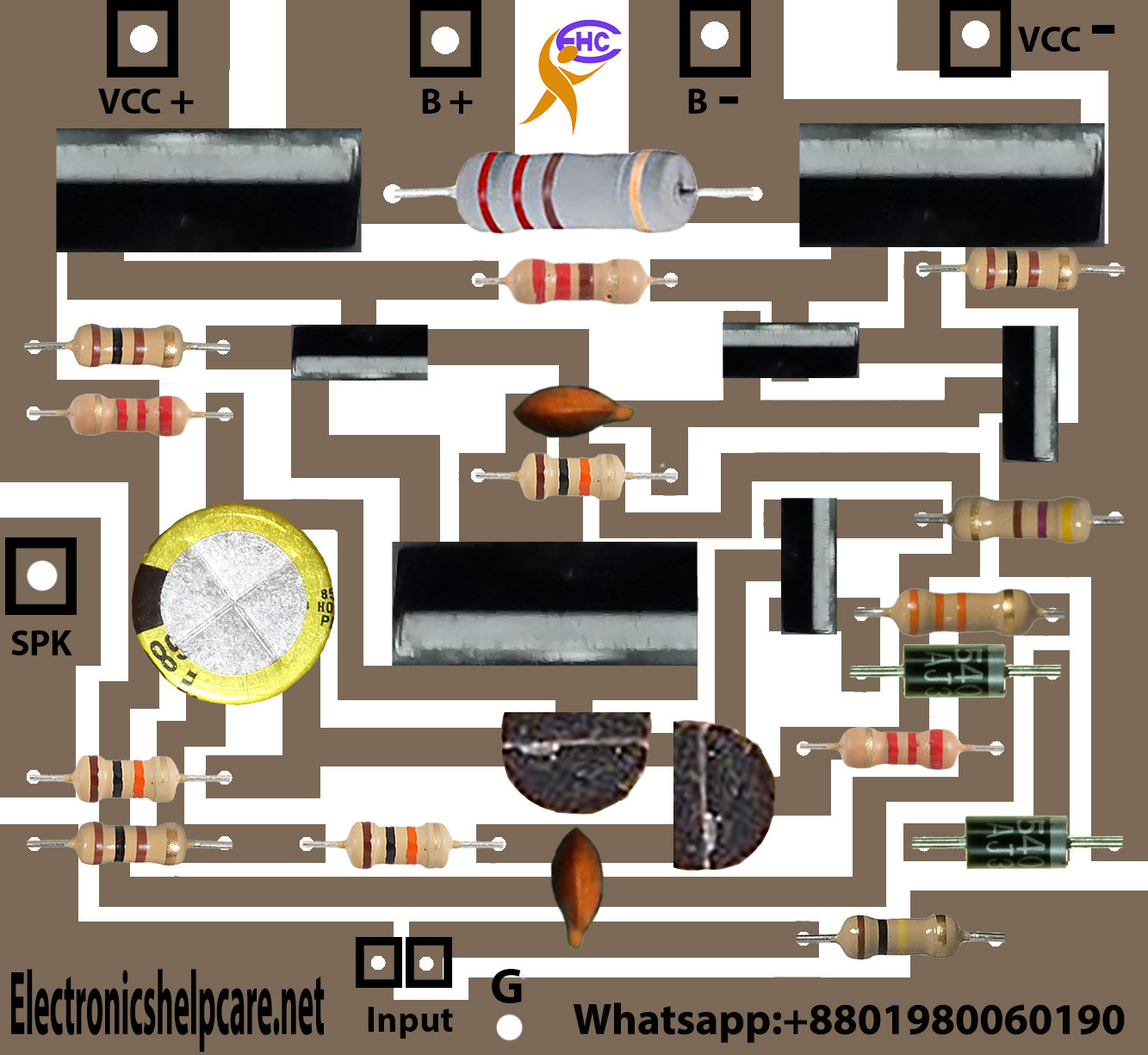
transistor amplifier circuit diagram Electronics Help Care
The transistor, as we have seen in the previous chapter, is a three-terminal device. Representing the basic amplifier as a two port network as in figure 9.1, there would need to be two input and two output terminals for a total of four. This means one of the transistor terminals must be common to both the input and output circuits.
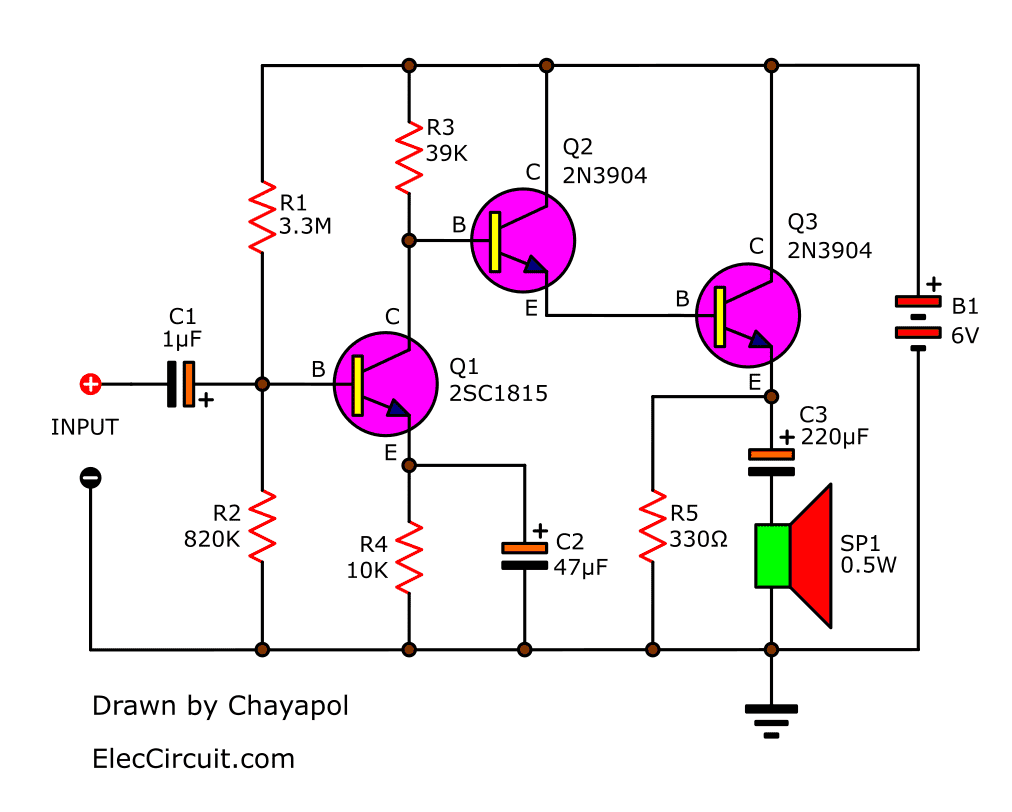
Very simple amplifier circuit using transistor 2N3904
This electronics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the Class A, AB, B, and C transistor amplifiers. The class A amplifier is the common emit.
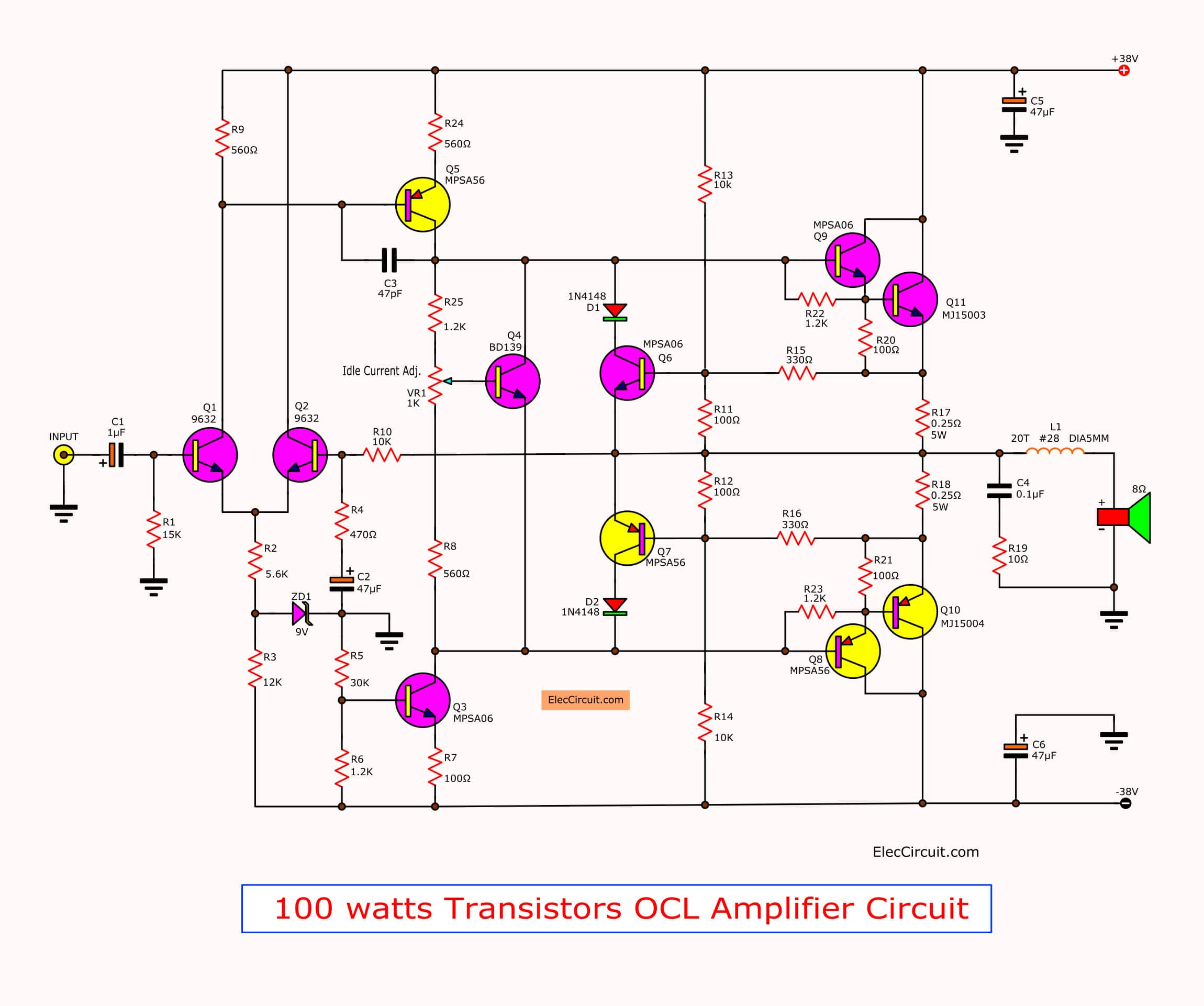
Transistor Power Amplifier Schematics
A transistor can take in a very small weak signal through the base junction and release the amplified signal through the collector. Transistor amplifiers are used frequently in RF (radio frequency), OFC (optic fibre communication), audio amplification, etc. In this lesson, we will discuss how a transistor works as an amplifier.

Simple Transistor Amplifier Circuit Diagram Wiring Digital and Schematic
The transistor amplifier circuit diagram typically includes the transistor itself, along with other passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors. These components are arranged in a specific configuration to achieve the desired amplification of an input signal. The circuit diagram also shows the power supply connections.
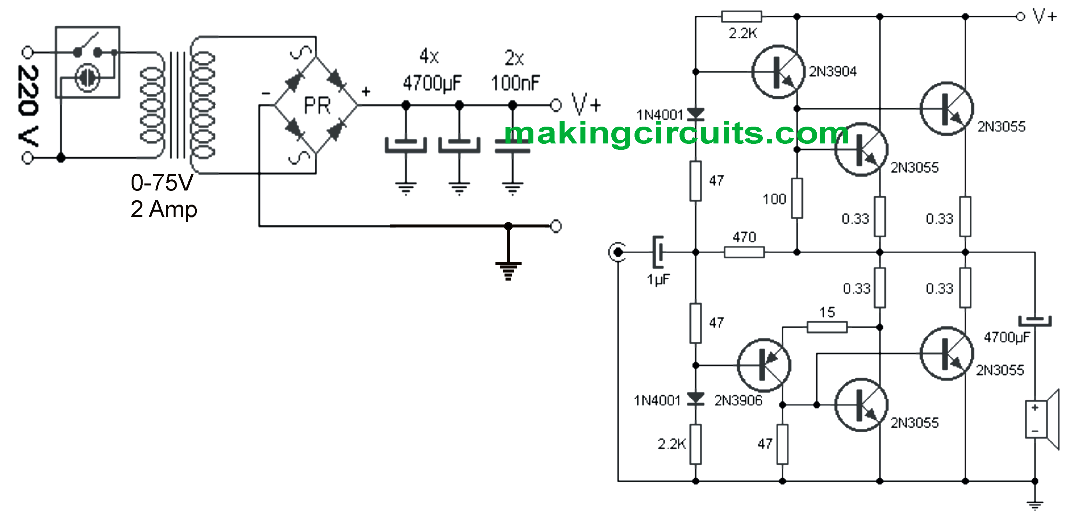
Simple 100 Watt Amplifier Circuit using 2N3055 Transistors
Take a look at these circuits. Maybe you get the idea of it. Table of Contents hide The Simple Audio Amplifier circuits without ICS 2N3904 transistor simple amplifier circuit 3 transistors power amplifier circuit Low Impedance Mini Amplifier Power Amplifier OTL using AC176+AC126 Power Amplifier OTL Cassette Radio Booster using TIP41+TIP42

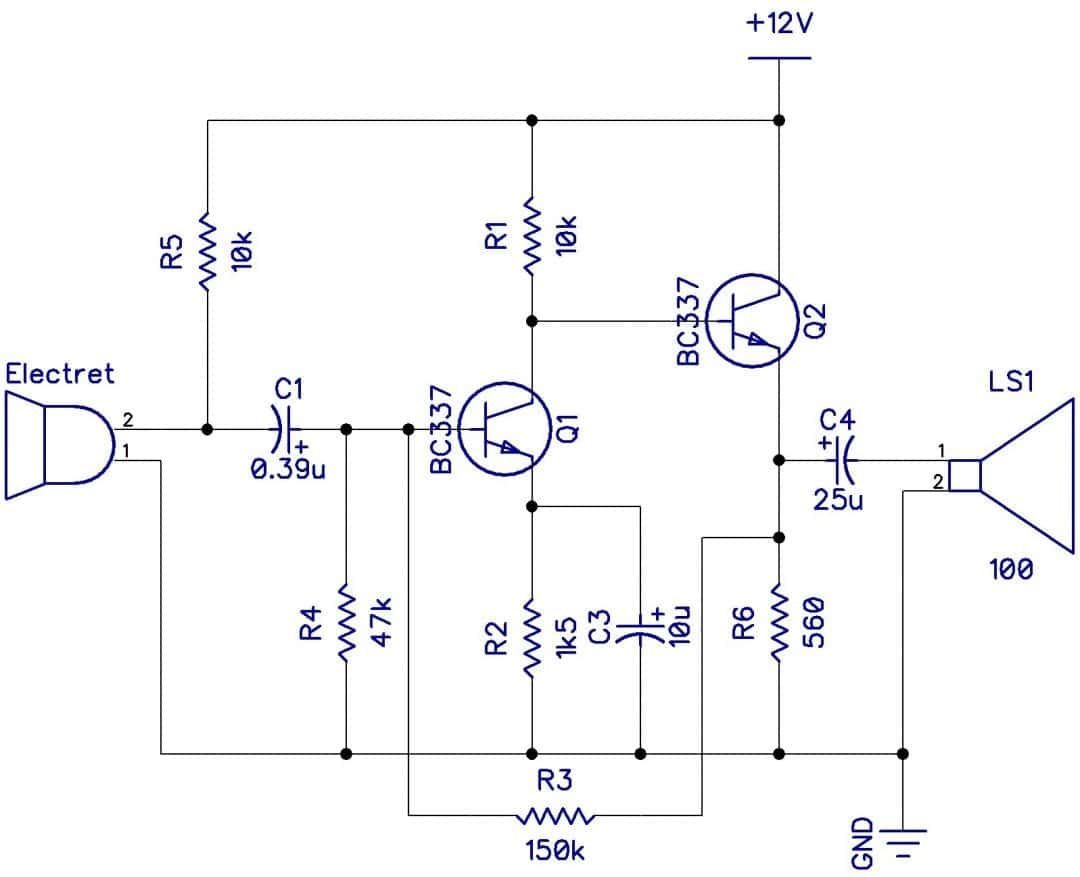
Simple Single Transistor Audio Amplifier Circuit
7.2 INTRODUCTION. The single transistor amplifier is one of the major keys to understanding the. analysis and design of all analog electronic systems. Stereos, television sets, radios, long. distance telephone communication circuits, and many other practical systems employ. principles that we will explore in this experiment.
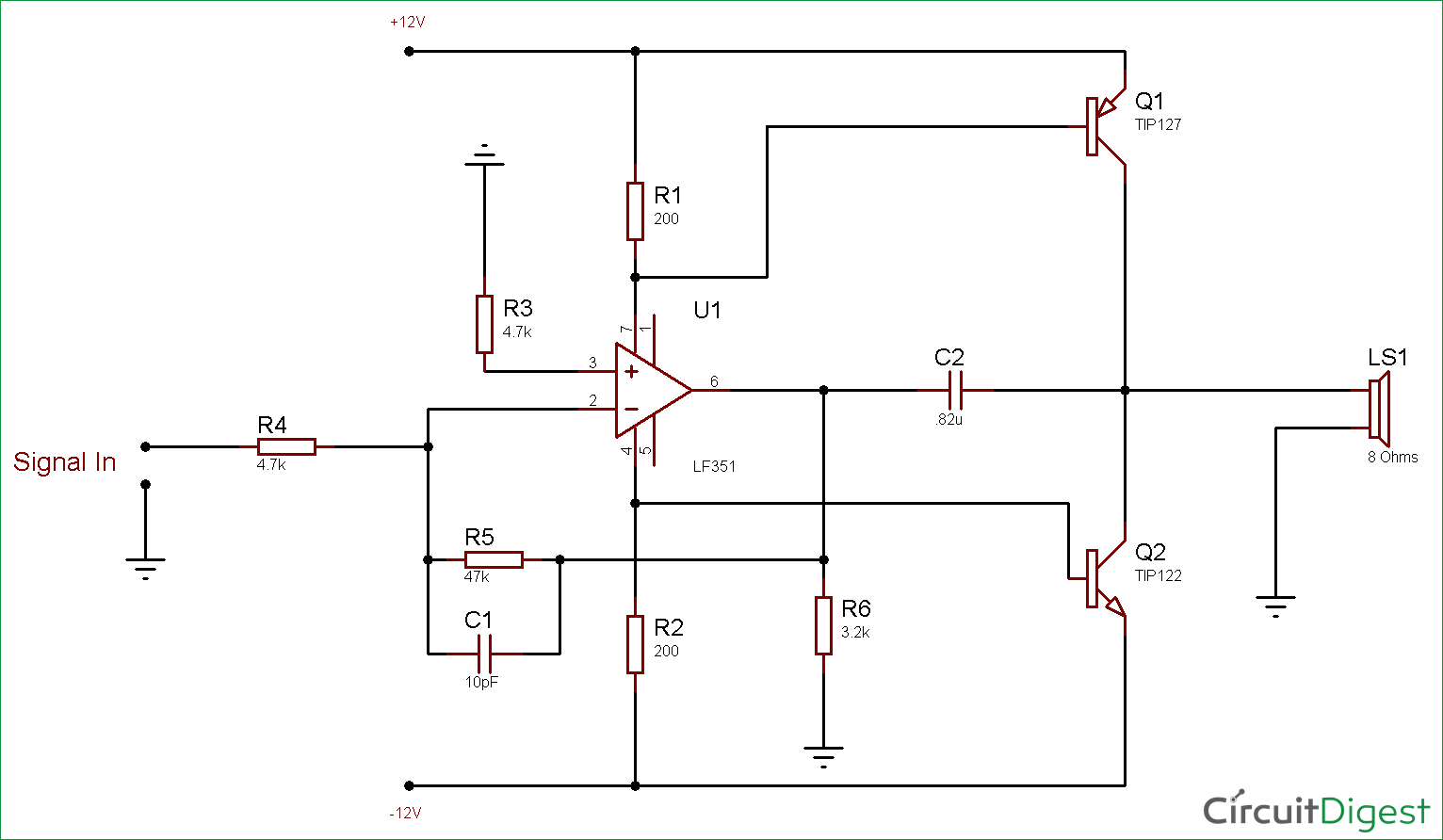
10 Watt Audio Amplifier Circuit Diagram using OpAmp and Power Transistors
An amplifier is a circuit that takes an electronic signal at its input and produces a larger signal at its output. This generally refers to voltage, but it could also be current, noise, or power. In this article, we will look at the most common and useful voltage amplifiers.
Transistor Amplifier Circuit with Diagram for 12 Watts
Transistor Amplifier Circuits Unit 1 - Introduction to Transistor Amplifiers 2 NEW TERMS AND WORDS Multistage - an amplifier circuit that uses more than one active component (transistor). active component - a circuit component that controls gain or directs current flow. gain - the amount by which an amplifier increases signal voltage, current, or power; expressed as

2 Stage Amplifier Circuit using Transistors Electronics Infoline
The process of raising the amplitude of a weak signal without change in its frequency and shape is known as 'amplification". In order to achieve this, the input circuit of the transistor remains forward biased and the output circuit always remains to reverse biased during all parts of the signal this is known as 'transistor biasing'.

Max Circuit Transistor As A Amplifier Circuit Diagram Pdf
In electronics, amplifiers have been used since the early twentieth century. Amplification can be accomplished using vacuum tubes or semiconductor devices such as transistors or integrated circuits.. The amount of amplification in a circuit is known as gain.The gain is the ratio between the strength of the output (current, voltage, or wattage) and the strength of the input (current, voltage.
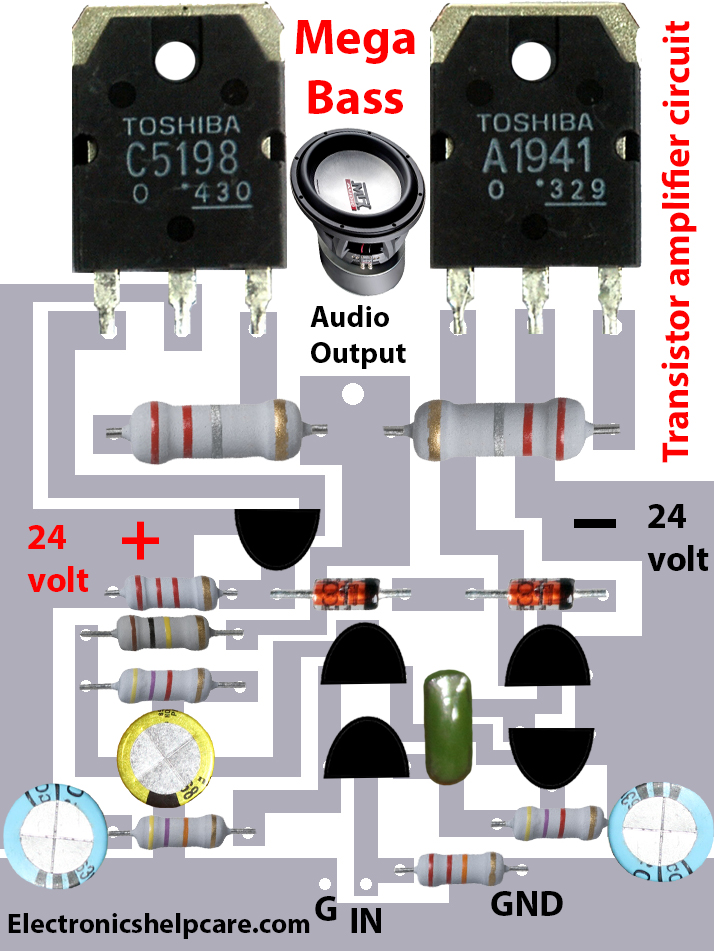
how to make transistor amplifier? Electronics Help Care
The three basic transistor amplifiers circuit diagram: common-emitter transistor amplifier, common-base transistor amplifier, and common-collector transistor amplifier. Transistors are manufactured with two or three leads extending from their case. See Figure 4. These packages are accepted industry-wide regardless of manufacturer.

Simple Single Transistor Audio Amplifier Circuit
Simple Transistor Amplifier Circuit Diagram . Working of Transistor as an Amplifier. In the above circuit diagram, we have made a voltage divider circuit using resistor R1 and R2 of 4.7k and 1.5k respectively. Hence, the output of the voltage divider circuit is used for proper biasing to turn ON the transistor. A transistor's base terminal.
Transistor Amplifiers Circuit Basics
2N3055 and MJ2955 are commonly used in Class AB amplifier circuits due to their high current and voltage handling capabilities. The 2N3055 is an NPN transistor while MJ2955 is a complementary PNP device. These transistors are generally used in power amplifiers and voltage regulators due to their high gain and high current capacity.
Transistor as an Amplifier Working and Circuit Diagrams Electronic Clinic
1. Intercom Circuit. 2. Audio Level Meter. 4. IR Headset. 5. How to Convert CD ROM to Audio CD Player. A simple transistor amplifier circuit diagram and schematic which can be used as a 12 watts audio transistor amplifier.An op amp IC is used to produce the gain required.