DC Motor Working Principle StudiousGuy
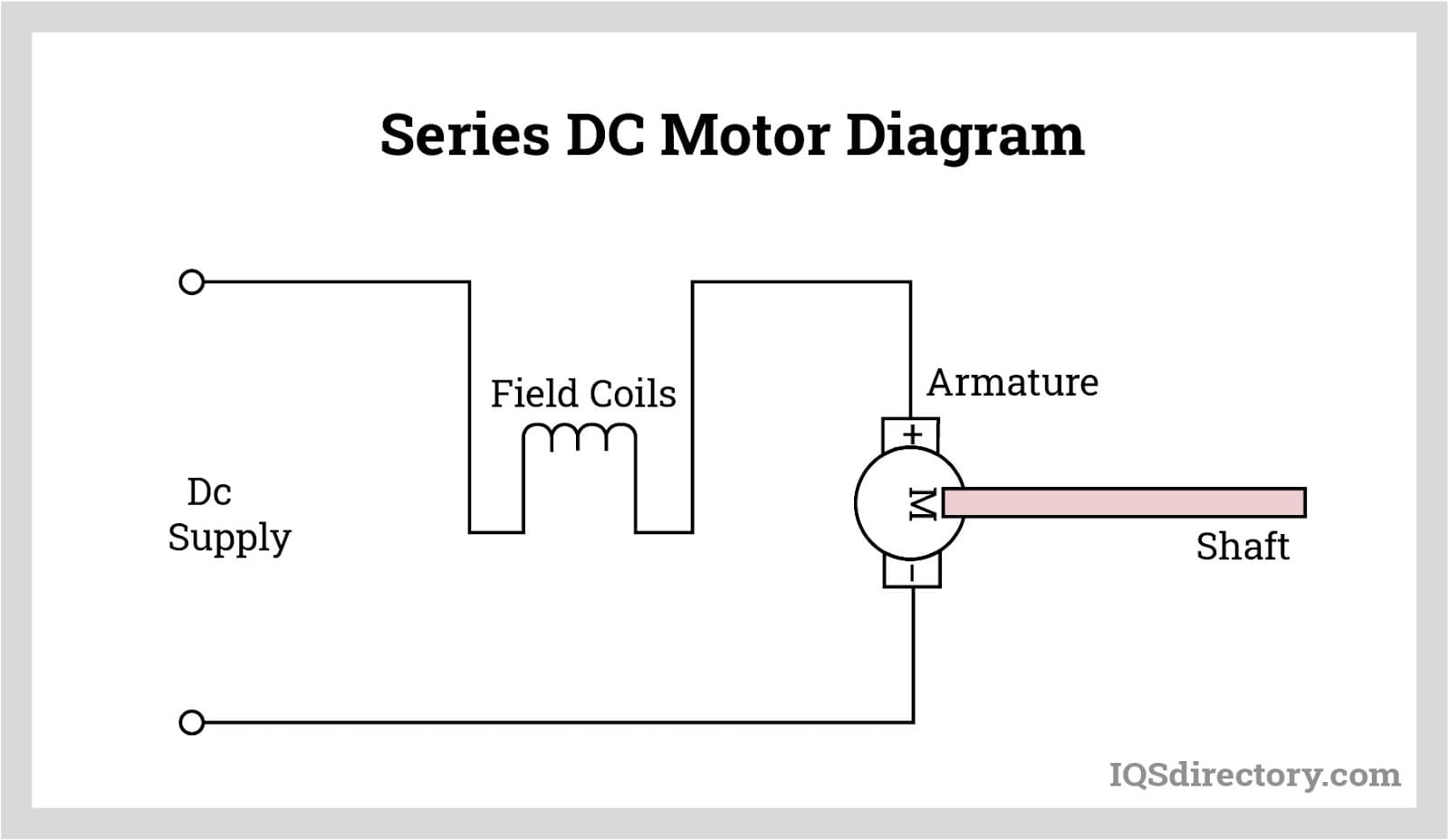
DC Series Motor : Circuit Diagram, Characteristics and Its Applications DC Series Motor Working and Its Applications There are two types of DC motors based on the construction such as self-excited, and separately excited. Similarly, self-excited motors classified into three types namely DC series motor, DC shunt motor, and DC compound motor.
Electric Engine Diagram With Labels
Physics Current Electricity DC Motor DC Motor A DC motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. In a DC motor, the input electrical energy is the direct current which is transformed into the mechanical rotation. In this session, let us know what is a DC motor, types of DC motor and their applications.

3 Model of a brush DC motor Download Scientific Diagram
4 Learn how a DC motor works to understand the basic working principle of a DC motor. We consider conventional current, electron flow, the winding, armature, rotor, shaft, stator, brushes, brush arms, terminals, emf, electromagnets, magnetic attraction as well as detailed animations for how the dc motor works.

All About Shunt DC Motors What They Are and How They Work
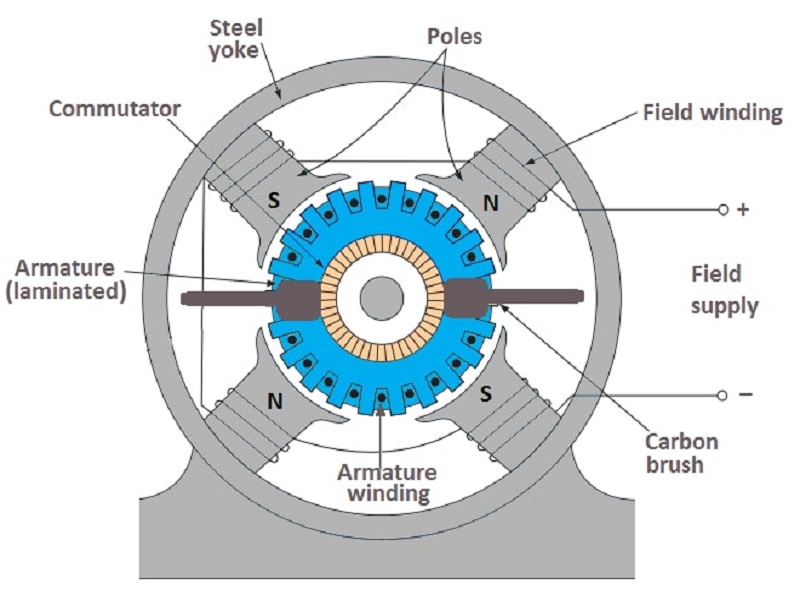
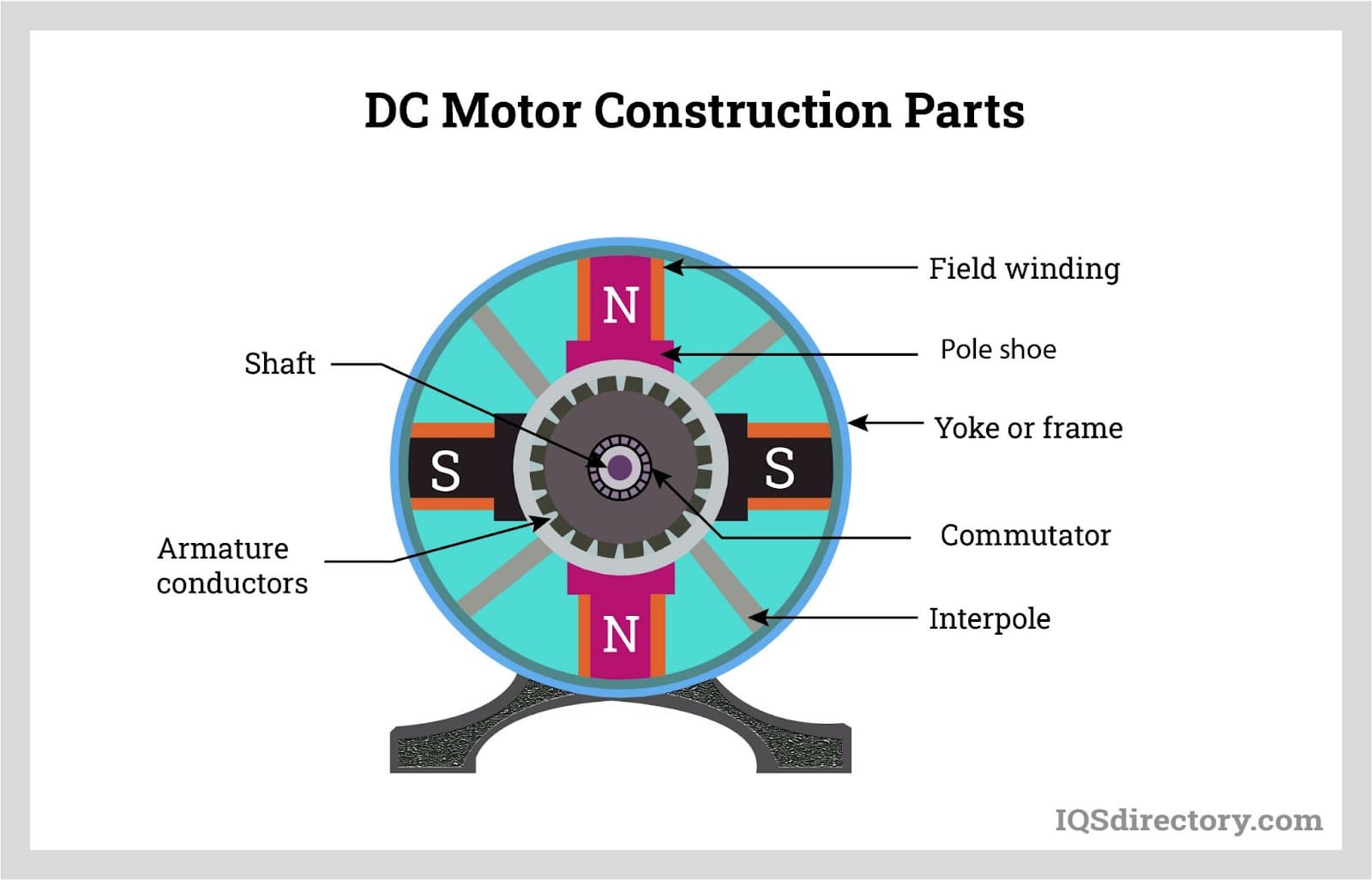
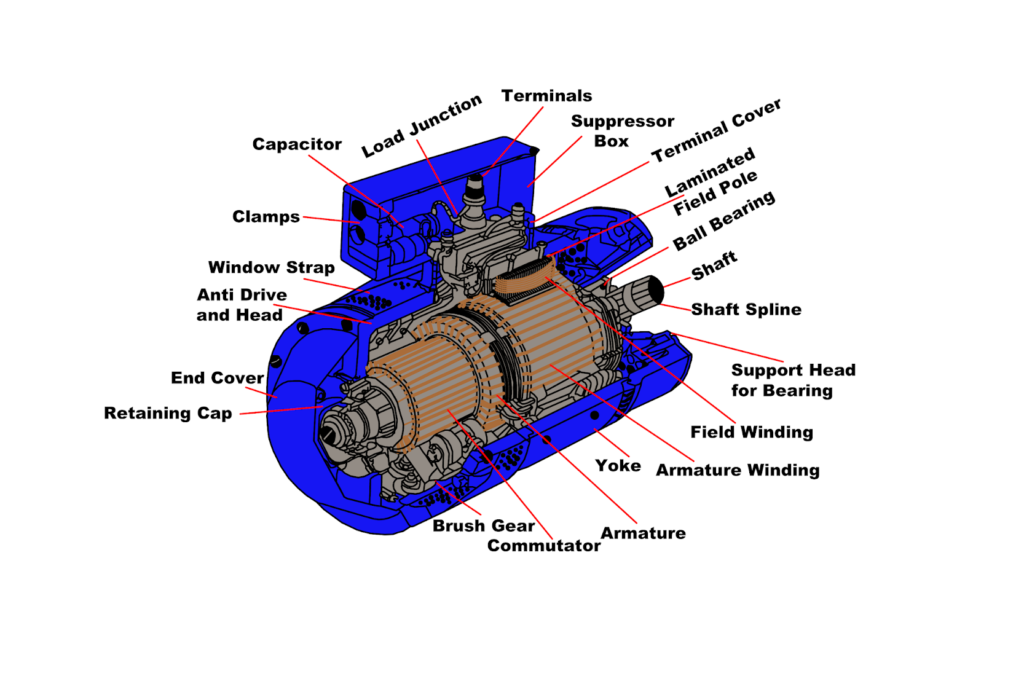
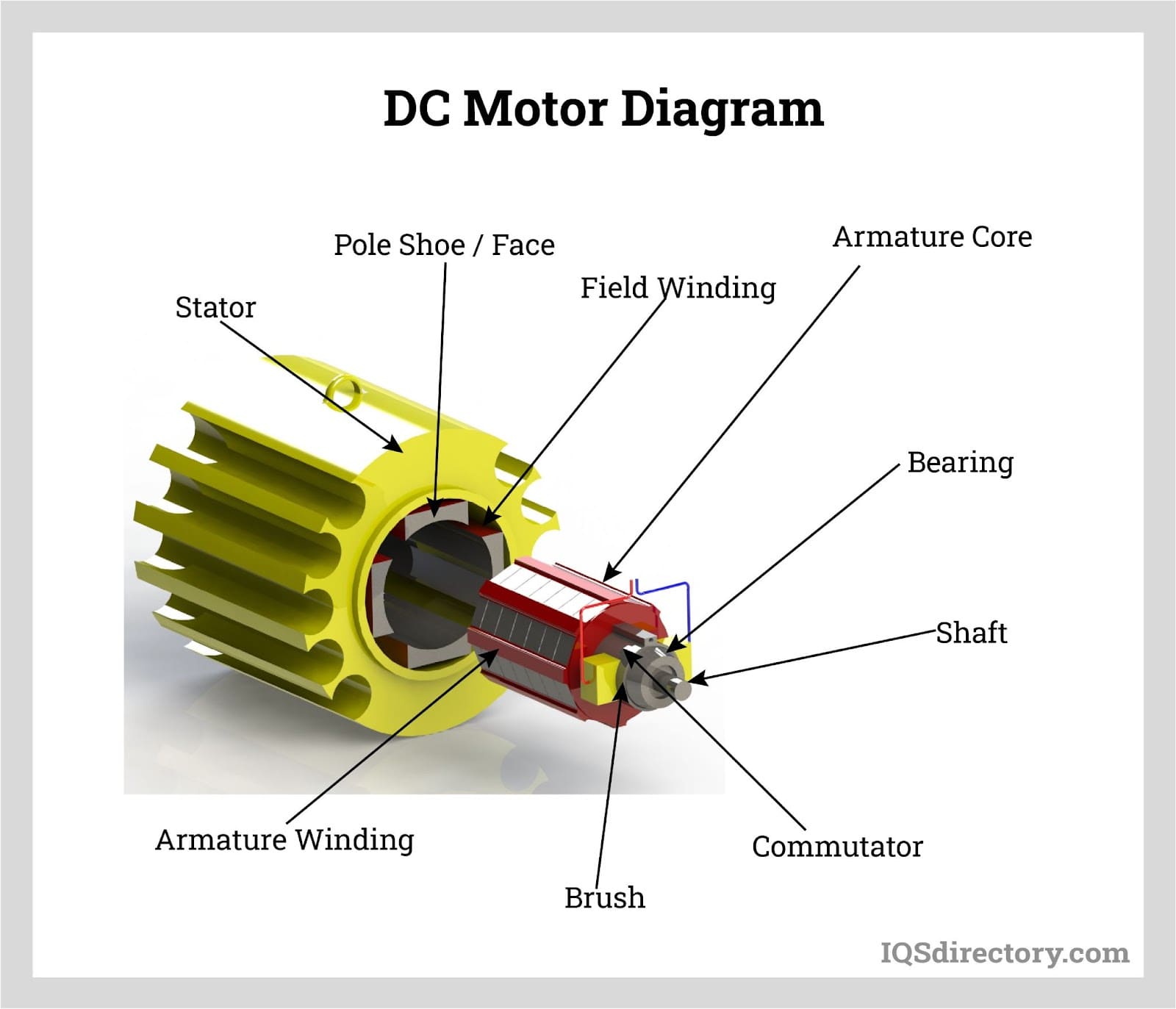
This article mainly covers DC Motor Construction and its Parts with labelled diagrams. Furthermore, a cutaway view of the DC Motor is presented and discussed in detail. The main parts of a typical DC motor are: field frame or yoke end-shields and bearings field poles field coils armature and commutator brush gear and brushes.
DC Motor What Is It? How Does It Work? Types, Uses
A simple way to control the speed of a DC motor is to regulate the supply voltage with pulse width modulation (PWM). Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) The basic idea behind PWM is that it switches the supply voltage ON and OFF very quickly. By adjusting the length of the ON/OFF pulses, we can set the voltage to anywhere between 0V and the maximum.
What Is It? How Does It Work? Types, Uses (2022)
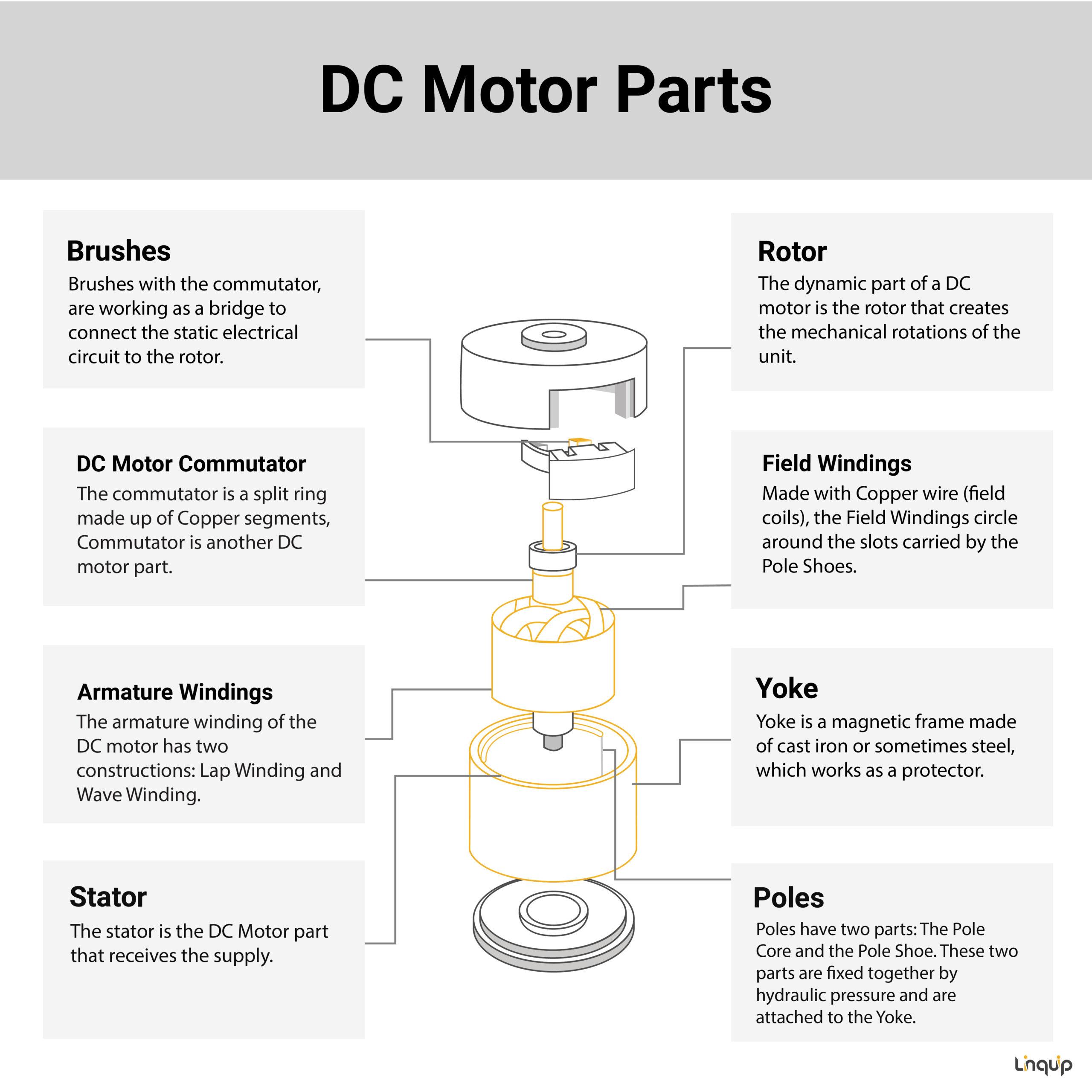
A Yoke. Poles. Field windings. Armature windings. Commutator. Brushes. A stator is the static part of the DC machine that houses the field windings and receives the supply. A rotor is the rotating part of the DC machine that brings about the mechanical rotations. All these parts put together make up the total construction of a DC motor.
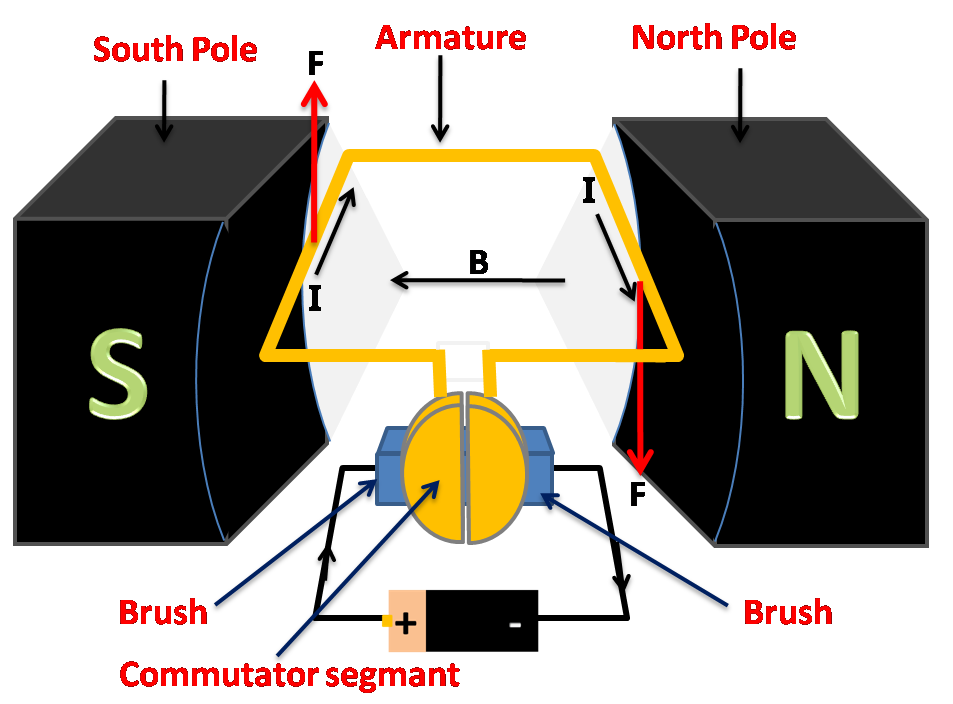
MRITS ECE BLOG HOW DOES A DC MOTOR WORK?(click on the diagrams to get clarity)
In your house, almost every mechanical movement that you see around you is caused by an AC (alternating current) or DC (direct current) electric motor. In this article we'll look at both types. By understanding how a motor works you can learn a lot about magnets, electromagnets and electricity in general.
8 Different DC Motor Parts, Structure, Design and Advantages + PDF Linquip
A DC motor or direct current motor is an electrical machine that transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy by creating a magnetic field that is powered by direct current. When a DC motor is powered, a magnetic field is created in its stator. The field attracts and repels magnets on the rotor; this causes the rotor to rotate.

Wonderful Labelled Diagram Of Dc Motor 2006 Chevy Equinox Aftermarket Stereo Wiring Harness
The DC motor diagram shows the most important components of the device. It consists of the Armature (rotating part), the yoke, field windings, carbon brushes, and the commutator. Stator The stator is the DC motor's stationary component. Its primary function is to serve as the device's solid outer frame and to generate a magnetic field.
Working Principle of DC Motor StudyElectrical Online Electrical Engineering Learning Site
A DC motor is an electromechanical energy conversion device, which converts electrical energy input into the mechanical energy output. The operation of the DC motor is based on the principle that when a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, a mechanical force acts on the conductor. The magnitude of the force is given by,
8 Different DC Motor Parts, Structure, Design and Advantages + PDF Linquip (2023)
Contents: Separately Excited DC Motor Self Excited DC Motor Shunt Wound Motor Series Wound Motor Compound Wound Motor Separately Excited DC Motor As the name signifies, the field coils or field windings are energised by a separate DC source as shown in the circuit diagram shown below: Separately Excited DC Motor Self Excited DC Motor

Dc Motor Wiring Diagram 2 Wire
DC Direct Current Motor Types and Connections The illustrations below schematically show the different methods of connecting the field and armature circuits in a DC motor. The circular symbol represents the armature circuit, and the squares at the side of the circle represent the brush commutator system.
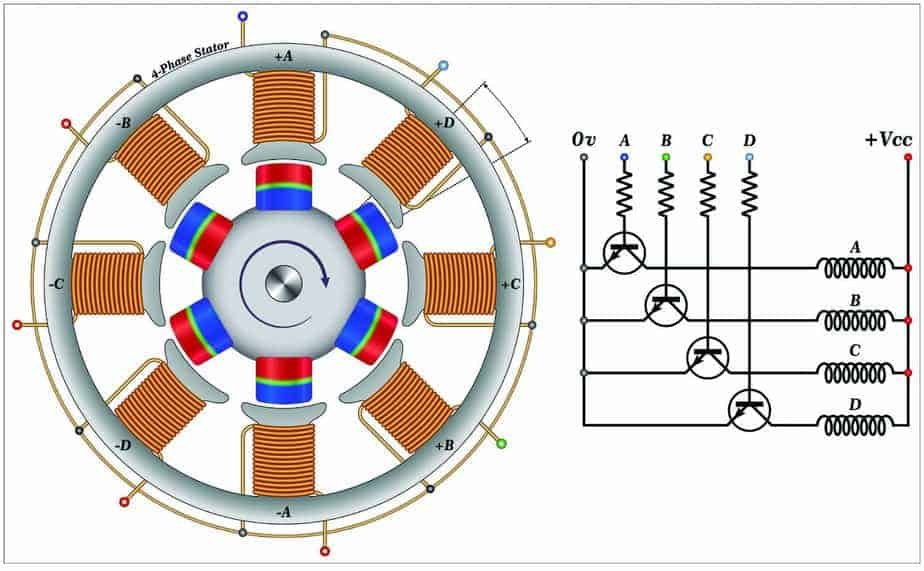
What is a Brushless DC Motor Overview and Advantage Saw Features
Field-Oriented Motor Control (FOC): Bridging the Gap Between DC and PMS Motors. In-depth electrical analysis of the Direct Current (DC) Motors highlights the capability to control the excitation of both stator and rotor independently. This independent control mechanism ensures that torque generation and magnetic flux can be distinctly adjusted.

DC Motors Explained Advantages of Brushed & Brushless Motors YouTube Mechanical energy
A DC motor is composed of the following main parts: Field coil or stator This is a non-moving part of the magnetic circuit on which a winding is wound in order to produce a magnetic field. The electro-magnet that is created has a cylindrical cavity between its poles. Armature or rotor
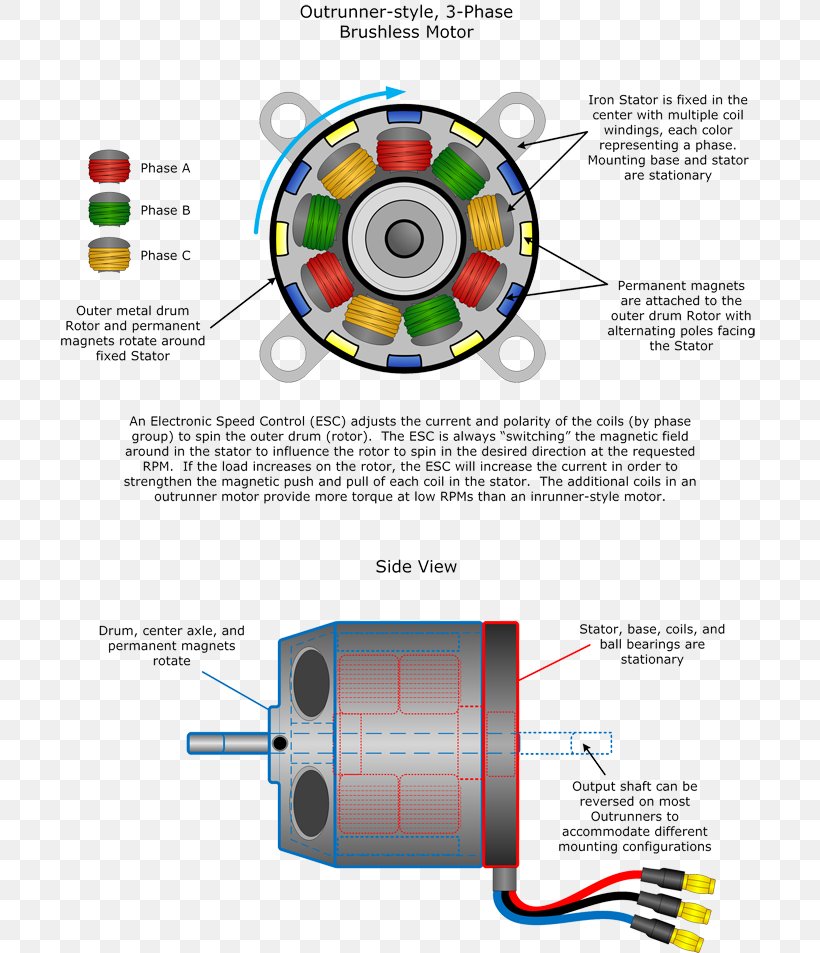
Brushless DC Electric Motor Engine Diagram Quadcopter, PNG, 700x953px, Brushless Dc Electric
DC motors are devices designed to convert direct current electrical energy to mechanical energy! This rotary electrical device has different types, all of them containing either electronic internal mechanism or electromechanical internal mechanism responsible for changing the direction of current in the motor. See All DC Motor Experts
DC Motor Manufacturers DC Motor Suppliers
A DC motor is an electrical motor that uses direct current (DC) to produce mechanical force. The most common types rely on magnetic forces produced by currents in the coils. Nearly all types of DC motors have some internal mechanism, either electromechanical or electronic, to periodically change the direction of current in part of the motor.